INTRODUCTION
Fish and other seafood are one of the most perishable food items because of their high water, protein and fatty acid content, which the spoilage microflora need to growth [Chan et al., 2021a; Surówka et al., 2021]. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) is a substantial aquacultural fish species, with its high nutritional value making it a popular food for consumers worldwide. However, this nutritient content can also limit the shelf-life of the product [Chan et al., 2021b; Kritikos et al., 2020]. The biochemical and enzymatic reactions which occur in fresh salmon from the time of capture trigger autolysis, oxidation and enhanced microbial growth, all leading to a rapid spoilage [Chan et al., 2021a]. The lipid oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, the oxidation of protein and non-protein nitrogenous compounds, and growth of spoilage organisms are the main factors reducing the shelf-life of fresh salmon, thereby generating off-flavor and off-odor that influence the consumer’s acceptance [Merlo et al., 2019]. Furthermore, the formation of biogenic amines in fish is directly related to the growth of spoilage microorganisms [Çelebi Sezer et al., 2022; Houicher et al., 2021].
Biogenic amines are nitrogenous compounds with heterocyclic, aromatic and aliphatic chemical structures generated by microbial decarboxylation of free amino acids [Arulkumar et al., 2023; Çelebi Sezer et al., 2022]. Histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, tyramine, spermine and spermidine are the most important biogenic amines found in food. Enterobacteriaceae, Clostridium spp., Aeromonas spp., Aerobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., Shewanella spp., Lactobacillus spp., Photobacterium spp., Morganella morganii, yeast and mold are among the microorganisms responsible for the deterioration of salmon and the formation of biogenic amines [Arulkumar et al., 2023; Powell & Tamplin, 2012]. The composition of food, the microbial flora and parameters (i.e., temperature) that promote bacterial growth, packaging and storage time, influence the amount and type of biogenic amines formed [Dadáková et al., 2009]. Therefore, it is imperative to use chilling methods in order to preserve the quality of fresh fish from the moment it is caught until it is offered for consumption [Surówka et al., 2021].
Packaging techniques applied in combination with low-temperature storage offer an effective practice for extending the shelf-life of fresh fish and fishery products [Chan et al., 2021a; Kritikos et al., 2020]. Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) is the most preferred preservation method allowing to manipulate the content of gas mixtures (O2, CO2, N2, etc.) in the packages before sealing them with a permeable film to retard the enzymatic and chemical reactions [Chan et al., 2021b]. Studies conducted so far have shown that, depending on fish species and storage temperatures, modified atmosphere packaging extends the shelf-life of seafood and its products compared to air packaging [Powell & Tamplin, 2012; Sivertsvik et al., 2003; Tsironi & Taoukis, 2018; Zhang et al., 2022]. Besides all these, the composition of a gas mixture used in MAP is critical to ensure a high-quality product and varies depending on the species of fish [Cooksey, 2014]. For fatty fish species such as salmon, the use of higher CO2 levels with lower or without O2 is inevitable to reduce oxidative rancidity and the growth of bacteria [Chan et al., 2021b; Merlo et al., 2019]. In addition, carbon monoxide (CO) is an alternative gas used at low levels (0.3 to 0.5%) with 60 to 70% CO2 and 30 to 40% N2 in modified atmosphere packaging to ensure color stability, suppress microbial growth, prevent oxidation and discoloration of the bones, and improve flavor acceptability [Cooksey, 2014; Cornforth & Hunt, 2008; Djenane & Roncalés, 2018].
Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the biogenic amine contents and quality parameters affecting the shelf-life of Atlantic salmon fillets packaged with a low level of CO (0.4%) and varied concentrations of CO2 during 27-day cold storage at 1°C.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Preparation of salmon samples
Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) was purchased from a chain branch of an international company that sells fish in three independent dates and transported to the laboratories within 2 h in polystyrene boxes containing dry ice. A total of 36 whole salmons (each weighing about 6–7 kg) were obtained 24–48 h post-catch and kept under cold storage until processing.
Each batch of 12 whole salmons was manually filleted after the tail, head, belly and backflaps were removed. Then, the filleted salmon samples were portioned into equal portions weighing approximately 200±50 g. Approximately 300 slices of salmon were randomly selected and placed on trays with two slices of salmon each.
Packaging salmon fillets
The salmon fillets of each group were placed on low O2 permeable (8–12 cm3/m2/24 h at standard temperature and pressure, STP) polyethylene terephthalate trays in portions of approximately 400±50 g (two slices of salmon per tray) and were heat-sealed with a low O2 permeable (3 cm3/m2/24 h) lidding film (Wrap Film Systems, London, UK) using a Ponapack VTK 40 SC Tray sealer (Ponapack, İstanbul, Turkey).
The ambient air was used for air packaging, while gas mixtures of CO, CO2 and N2 (in the percentage ratio of 0.4/30/69.6); CO2, N2 and O2 (in the percentage ratios of 40/30/30, 50/30/20, and 60/30/10); and CO2 and N2 (in the percentage ratio of 40/60), purchased in Linde Gas (Kocaeli, Turkey), were applied for modified atmosphere packaging. Codes of salmon fillet groups corresponding to each gas mixture used in packing are given in Table 1. All packages were stored at 1±1°C for up to 27 days, and salmon fillets were analyzed on days 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24 and 27. On each analysis day, a total of 2 packages were allocated, one tray for sensory analysis and other tray for quality analysis. The gas ratios of all packages were measured before opening on each analysis day using a PDI Dansensor A/B gas meter (PBI-Dansensor A/B, Ronnedevaj 18, DK 410, Ringsted, Denmark). Each experimental trial was performed in triplicate on different times.
Table 1
Composition of gas mixtures used in the packaging of salmon fillets.
Microbiological analyses
Total aerobic mesophilic bacteria (TAMB), total psychrotrophic bacteria (PsB), Enterobacteriaceae, lactic acid bacteria (LAB), Pseudomonas spp., Brochothrix thermosphacta and yeast-mold counts were determined in accordance with the related International Organization for Standardization method no. 6887-1 [ISO, 2017a]. Microbiological analyses were performed using 25 g of salmon samples for each group mixed with 225 mL of sterile peptone water in stomacher bags. After homogenization, serial dilutions were prepared to analyze relevant microorganisms.
Total aerobic mesophilic and psychrotrophic bacteria counts of salmon fillets were enumerated on plate count agar (Oxoid, CM0463, Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK) using ISO methods no. 4833-1 [ISO, 2013] and no. 17410 [ISO, 2019], respectively. Enterobacteriaceae counts were detected on violet red bile glucose agar (Oxoid, CM0485), lactic acid bacteria on de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) agar (Oxoid, CM0361), Pseudomonas spp. on Pseudomonas agar (Oxoid, CM0559 and SR0103) supplemented with cetrimide-fucidin-cephalosporin (CFC), B. thermosphacta on streptomycin tallous acetate actidione (STAA) agar (Oxoid, CM0881) with STAA selective supplement and yeast-mold counts on dichloran rose Bengal chloramphenicol (DRBC) agar (Oxoid, CM0727) according to ISO methods no. 21528-2 [ISO, 2017b], no. 15214 [ISO, 1998], no. 13720 [ISO, 2010], no. 13722 [ISO, 2017c] and no. 21527-1 [ISO, 2008], respectively. Microbial counts were expressed as log CFU/g.
Determination of biogenic amine content
The content of biogenic amines (histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, tyramine, spermine, spermidine) was detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using the Agilent system (Agilent Technologies, St. Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a diode array detector (G1315B DAD), in accordance with the method described by Bogdanović et al. [2020].
The reagents, all eight biogenic amines and analytical column were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and all were of HPLC grade (purity 98–99%). A homogenized salmon sample (5 g) was extracted with 0.4 M perchloric acid, and the filtrate was alkalized by the addition of 200 μL of a 2 M NaOH solution. After subsequent steps, 2 mL of a dansyl chloride solution was added, and the mixture was incubated (at 40°C for 45 min). The remaining dansyl chloride was removed and kept in darkness (45 min). The total volume was made up to 5 mL with acetonitrile, and the mixture was filtered through a 0.45 μm syringe filter (Sartorius, Gottingen, Germany). The separation of biogenic amines was carried out using a LiChrospher C18 analytical column (250×4.0 mm, particle size 5 μm) with an injection volume of 20 μL. HPLC conditions were applied according to the procedures described by Bogdanović et al. [2020]. The calibration curves covering eight concentrations ranging from 0.25 mg/kg to 500 mg/kg were used to quantify biogenic amines. The mean content of individual amines in salmon fillets was expressed as mg/kg.
Chemical analyses
Measurement of pH, water activity and moisture content
The pH of salmon fillets was measured with a digital pH meter (Hanna HI-9321, Woonsocket, RI, USA) calibrated with pH 4.0 and 7.0 solutions at room temperature. The water activity (aw) of salmons was determined by using an aw meter (Decagon AquaLab LITE, Washington, USA). The moisture content of salmon fillets was specified by drying a homogeneous mixture at 105±2°C to a constant weight [AOAC, 2005].
Determination of thiobarbituric acid reactive substance value
The thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) value of salmon fillets was detected by measuring the absorbance of color developed at 530 nm using a T80+ UV/VIS spectrometer (PG Instruments Ltd., London, UK). In accordance with the method described by Shrestha & Min [2006], the samples were extracted with trichloroacetic acid (TCA) and then treated with a thiobarbituric acid (TBA) reagent. The TBARS value was expressed as mg of malondialdehyde (MDA) per kg.
Determination of trimethylamine nitrogen value
Trimethylamine nitrogen (TMA-N) content of salmon fillets was determined according to the AOAC [2000] procedure by homogenizing salmon samples (10 g) with 20 mL of a 7.5% TCA (w/v) solution and then centrifuging at 1,008×g for 15 min. After the subsequent analysis steps had been completed in accordance with the relevant method, the final content was measured at 410 nm using a spectrophotometer (PG Instruments Ltd). Results of TMA-N level determination were expressed as mg/100 g salmon fillet.
Determination of total volatile basic nitrogen value
The determination of total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) levels of salmon fillets was performed in accordance with the procedure described by Esteves et al. [2021] using the microdiffusion method of Conway & Byrne [1933]. Results of TVB-N level determination were expressed as mg N/100 g salmon fillet.
Instrumental color analysis
The surface color of skinless salmon fillets was measured by using a Color Flex HunterLab apparatus (Hunter Associates Laboratory Inc., Reston, VA, USA). Color coordinate values for L* (lightness), a* (redness) and b* (yellowness) were recorded on the average of four different areas (3×3 cm) of salmon fillets using diffuse illumination (D65 2° observer) with an 8 mm aperture and a 25 mm port size [AMSA, 2012]. The total color difference (ΔE) was calculated using Equation (1):
where: L* indicates lightness value at storage time and L0* indicates the initial lightness value of the sample; a* indicates redness value at storage time and a0* indicates the initial redness value of the sample; b* indicates yellowness value at storage time and b0* indicates the initial yellowness value of the sample.Sensory evaluation
The sensory evaluation of salmon fillets was carried out with a panel consisting of 12 panelists (age between 28 to 47 years, 7 men and 5 women) trained according to the ISO method no. 8586 [ISO, 2012] and experienced in seafood evaluation. Before the sensorial assessment, a preliminary session (1 h) was organized to define the sensory attributes in a round-table discussion using a standardized procedure no. 13299 [ISO, 2016] in two separate sessions. An open-discussion session was then held to familiarize the panelists with the attributes and the scale to be used.
The panelists evaluated four sensory attributes (color intensity, off-odor, appearance and tenderness) using a 9-cm unstructured linear scale, in which 1 (left side) referred to “pale color, putrid odor, stale and dull appearance, soft and pasty texture” and 9 (right side) referred to “strong color, typical fresh salmon odor, fresh and bright appearance, firm and succulent texture” for color intensity, off-odor, appearance and tenderness, following the method of Ouahioune et al. [2022].
The sessions were performed in individual booths under standardized laboratory conditions equipped in accordance with the ISO standard no. 8589 [ISO, 2007] on days 1, 3, 9, 15, 21 and 27 of salmon fillets storage. In each storage time, two salmon fillet samples of each of the seven packaging groups were served monadically as raw and coded with a three-digit number in randomized order.
The panelists received 7 independent sample sets, which included salmon samples served in closed cups immediately after the trays were opened for the evaluation of off-odor characteristics and samples on a plate for the assessment of other characteristics, on each day of analysis. Sensory panel was conducted in triplicate in two sessions.
Statistical analysis
The general linear model (GLM) procedure from SPSS 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) program was used to analyze the data for each parameter. The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted for each variable to determine the effects of packaging conditions and storage time. A Duncan’s test was used to check the significance of differences between and within groups for different days of storage, and differences were found significant at p<0.05. The data collected for sensorial evaluation was subjected to a Friedman test followed by a least significant difference test. The model used included the fixed effects of packaging conditions and storage time. All results were presented as means and standard errors (SE). Each experimental trial was repeated in triplicate on different times.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Physicochemical properties
The initial gas composition of packages contained 30.08%, 39.24%, 50.98%, 59.34%, 59.28%, 39.46% CO2 and 69.08%, 29.48%, 28.58%, 30.07%, 40.72%, 60.54% N2 for CO, 30% O2, 20% O2, 10% O2, 60% CO2 and 40% CO2 MAP groups, respectively. The CO2 level in the headspace composition of packages maintained relatively stable during storage time. On day 15 and 27 of storage, the CO2 levels of packages decreased to 24.62% and 21.49% for CO-MAP, to 50.43% and 45.79% for 60% CO2-MAP, to 34.28% and 29.65% for 40% CO2-MAP, while the CO2 concentrations increased to 43.45% and 47.76% for 30% O2-MAP, to 54.01% and 56.75% for 20% O2-MAP, and to 63.16% and 65.98% for 10% O2-MAP. The O2 concentrations were negligible under anaerobic conditions (CO and 40-60% CO2), while a slight decrease was observed in packages with low O2. The O2 level in gas composition of air packages decreased throughout the storage, resulting in an increase in CO2 concentration in the headspace (19.58% O2/2.46% CO2 on the first day to 12.56% O2/6.83% CO2 on day 27).
The pH of salmon fillets showed an increase parallel to the deterioration process during 27-day cold storage (Table 2). There was a significant (p<0.05) difference between packaging conditions in pH values throughout storage time except the 12th day. The samples packaged under CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP had significantly lower pH values than those packaged in air and 30% O2-MAP atmosphere (p<0.001). The pH value of air-packaged salmon showed a steady increase from 6.52 on day 15 to 6.94 at the end of storage, while the lowest value was recorded as 6.5 at the end of storage in 60% CO2-MAP and CO-MAP. The pH value, which starts to decrease in the post-mortem process due to rigor mortis, decreases further with CO2 decomposition in the package atmosphere. Subsequently, depending on storage time, an increase in pH value occurs due to microbial spoilage. This change in the pH value recorded in our study is similar to the observations made in other studies of Atlantic salmon packaged in a modified atmosphere [Fletcher et al., 2002; Milne & Powell, 2014; Sivertsvik et al., 2003]. The study of Chan et al. [2021b] also reported that modified atmosphere-packaged salmon samples had a significantly lower pH than the air-packaged ones, which is in line with our findings.
Table 2
Physicochemical properties of salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period.
[i] Composition of gas mixtures used in MAP of different groups of salmon fillets are shown in Table 1. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. Means within a column with different letters (a–e) are significantly different (p<0.05). Means within a row with different letters (A–H) are significantly different (p<0.05). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001; NS, not significant; aw, water activity; MAP, modified atmosphere packaging.
The water activity values and moisture content of salmons decreased through cold storage period in all packages (Table 2), with salmons packaged with air and 30% O2-MAP having lower aw values and moisture content than those packaged in 60% CO2-MAP and CO-MAP. There was a significant (p<0.05) difference between the air-packaged and MAP-packaged salmon throughout storage time.
Microbiological changes
Microbiological changes in salmon samples during cold storage are presented in Figure 1. The initial bacterial loads of salmon fillets were 3.00 log CFU/g, 3.81 log CFU/g, 0.69 log CFU/g, 4.20 log CFU/g, 3.74 log CFU/g, 3.58 log CFU/g and 3.00 log CFU/g for TAMB, PsB, Enterobacteriaceae, LAB, Pseudomonas spp., B. thermosphacta and yeast-mold counts, respectively.
Figure 1
Counts of total aerobic mesophilic bacteria, TAMB (A), total psychrotrophic bacteria, PsB (B), Enterobacteriaceae (C), lactic acid bacteria, LAB (D), Pseudomonas spp. (E), Brochothrix thermosphacta (F) and yeast-mold (G) of salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period. Different letters for each storage day indicate significant differences (p<0.05). Details regarding modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) are presented in Table 1.
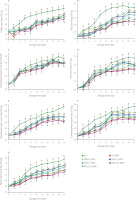
There was a significant difference between the air-packaged and modified atmosphere-packaged samples throughout storage time for psychrotrophic and mesophilic bacteria counts (p<0.001). The TAMB counts of modified atmosphere-packaged samples reached 5.90–7.30 log CFU/g at the end of the 27-day storage, while the PsB count reached 5.14–6.11 log CFU/g (Figure 1). The air-packaged samples had mesophilic and psychrotrophic bacteria counts of 7.89 and 7.64 log CFU/g, respectively, whereas a 2-log in-hibition was recorded in those packaged in CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP. There was also a significant difference in Enterobacteriaceae counts between the packaging groups (p<0.001) during storage except the 3rd day (p≥0.05), while an inhibition of 0.5 log was recorded in CO and 60% CO2-MAP compared to air packaging at the end of storage. The changes in LAB counts were close to each other during the 27-day storage period, but there was a significant difference of about 1 log between the air-packaged and modified atmosphere-packaged groups (p<0.05). The Pseudomonas spp. count of salmon fillets packaged with ambient air and 30% O2 exceeded 7 log CFU/g on days 15 and 24, respectively, while salmon packaged with 60% CO2 and CO did not reach this value even at the end of storage. The CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples had 1 log CFU/g lower bacterial count than the samples packaged with high O2, which was significantly different (p<0.001). A similar change was determined in B. thermosphacta counts of salmon fillets, and the bacterial counts of air-packaged samples were 1.0–2.3 log CFU/g higher than these recorded for the other groups at the end of storage (p<0.001). Yeast-mold counts reached 7.7 log CFU/g with a rise noted in the air-packaged samples during storage time, and an inhibition at a level of 2.0–2.2 log recorded in the CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples (p<0.001).
The study results indicate that salmon fillets stored in cold storage conditions undergo a deterioration process depending on storage time and packaging conditions. The salmon fillets packaged with ambient air entered a faster spoilage process than the products packaged with modified gas mixtures. This process was relatively slower in the samples packaged with high CO2 and low CO (<0.5%). Since fish and fishery products are highly susceptible to contamination and spoilage, storage in ambient air leads to a rise in microbial activity, especially when temperature increases [Chan et al., 2021b]. There are many studies supporting this scientific view that storage in ambient air accelerates microbiological activity in salmon, and this can be slowed down by modified atmosphere packaging resulting in product’s shelf-life extension [Fernandez et al., 2009; Qian et al., 2022; Saraiva et al., 2017; Sivertsvik et al., 2003].
Similarly to our study, Fernandez et al. [2009] reported that the changes in total bacterial counts of salmon packaged in modified atmosphere with different gas combinations were lower than those observed for the samples packaged with ambient air, which was also demonstrated by Qian et al. [2022]. The shortest shelf-life recorded for salmon was 16 days in 25% CO2/75% N2 package, while the longest shelf-life reached 22 days in 75% CO2/25% N2 packages [Fernandez et al., 2009]. Beside this, Qian et al. [2022] highlighted that CO2 content above 40% was found to effectively inhibit the growth of mesophilic bacteria. However, higher CO2 contents, such as 100% and 80%, did not have a greater inhibitory effect on bacteria as higher CO2 concentrations contribute to bacterial growth by increasing the solubility of muscle proteins [Qian et al., 2022]. In addition, similar changes in the count of psychrophilic bacteria were recorded with an effective suppression under a gas composition of 60% CO2/10% O2/30% N2 [Qian et al., 2022].
Likewise, Sivertsvik et al. [2003] observed enhanced bacterial growth in air-packaged Atlantic salmons compared to the modified atmosphere-packaged samples. In turn, Saraiva et al. [2017] found that the bacterial load of air-packaged salmon samples reached 7.16 log CFU/g on day 9 of storage, while the modified atmosphere-packaged samples remained below (6.36 log CFU/g) this level even on the 13th day. In this regard, the use of CO2 in modified atmosphere packaging retards microbiological growth by prolonging the lag phase and reducing the accumulation of degradation compounds, such as TVB-N and hypoxanthine [Chan et al., 2021b]. Moreover, De la Hoz et al. [2000] reported that the shelf-life of salmon steaks packaged under different CO2 concentrations was extended by 6 and 15 days for 20% and 40% CO2, respectively, compared to air packaging, and stated that the primary bacterial group responsible for the spoilage of salmon was Pseudomonas/Shewanella and the second one was Enterobacteriaceae. Saraiva et al. [2017] detected the yeast-mold counts at 7.23 log CFU/g on day 9 of storage in air-packaged salmon, while this level could not be overpassed (4.06 log CFU/g) in modified atmosphere packaging even on the 13th day of storage. Conformably, Brochothrix spp. and Carnobacterium spp. were reported to be the main bacterial groups detected in salmon packaged under 60% CO2 modified atmosphere and cold stored for 18 days. The high CO2 levels used in MAP reduce the count of aerobic bacteria, while CO2 levels in packages promote the growth of lactic acid bacteria, which are one of the organisms responsible for spoilage in salmon stored under modified atmosphere [Merlo et al., 2019].
Biogenic amine formation
The histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, tyramine, spermine and spermidine contents of salmon fillets packaged under modified atmosphere with different gas mixtures determined during the cold storage for 27 days are given in Figure 2. The levels of the mentioned biogenic amines increased significantly at the end of storage. Modified atmosphere packaging with different gas mixtures had significant effects on the formation of biogenic amines compared with air packaging (p<0.001). The lowest levels of the analyzed biogenic amines were found in the CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples, respectively.
Figure 2
Biogenic amine contents including histamine (A), cadaverine (B), putrescine (C), tryptamine (D), phenylethylamine (E), tyramine (F), spermine (G), spermidine (H) of salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period. Different letters for each storage day indicate significant differences (p<0.05). Details regarding modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) are presented in Table 1.
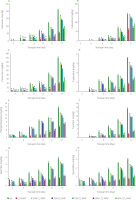
Cadaverine, tryptamine and tyramine were not detected in the salmon samples until the 6th day of storage, while histamine was detected only in the air-packaged samples; and putrescine, phenylethylamine, spermine and spermidine were detected in the modified atmosphere-packaged salmon except CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples on the 3rd day of storage. The histamine content of the air-packaged salmon samples exceeded 100 mg/kg on day 21 of cold storage, whereas this value was not reached even on day 27 of storage in CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP (Figure 2). Cadaverine was not detected in the CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples until the 9th day of storage, while it was detected at 61.84, 71.15 and 85.71 mg/kg in the CO-MAP, 60% CO2-MAP and 40% CO2-MAP samples, respectively, at the end of storage. For the air-packaged samples, this value reached 144.58 mg/kg on the last day. Even though the quantity of putrescine was below 50 mg/kg in all groups until day 15 of storage, it was recorded as 85 mg/kg in the air-packaged salmon and as 60–70 mg/kg in the 20% and 30% O2-MAP samples on day 21. Meanwhile, putrescine content was above 100 mg/kg on the last day of storage in the CO-MAP, 60% CO2-MAP and 40% CO2-MAP samples with a value of 39.19, 44.42 and 62.02 mg/kg, respectively. The amount of tryptamine remained below 10 mg/kg in all MA-packaged samples until the end of storage, only in the air-packaged samples it was recorded as 10.66 mg/kg on day 27. Phenylethylamine showed a similar change to tryptamine, reaching a value of 15.68 mg/kg on the 27th day of storage in the air-packaged salmon. The highest content of phenylethylamine recorded in the CO-MAP sample was 5.66 mg/kg, while values of 7.01 mg/kg and 7.36 mg/kg were determined in the 40% and 60% CO2-MAP samples, respectively. Similarly to phenylethylamine and tryptamine, the tyramine contents were determined as 13.44 mg/kg and 10.79 mg/kg on the last day of storage in the air-packaged and 30% O2-MAP samples, respectively. However, the amounts of tyramine remained below 10 mg/kg in the 10% and 20% O2-MAP samples, whereas in the salmon samples packaged with CO and high CO2 they were in the range of 1.66 to 3.03 mg/kg until the end of storage. The spermine and spermidine contents did not reach even 4 mg/kg until the end of storage in all packages, with values determined in the CO-MAP and high CO2-MAP samples below 1.5 mg/kg even at the end of storage.
The formation of biogenic amines can be affected by many factors such as handling, processing and storage conditions, as well as the existing bacterial load in seafood, i.e., raw material quality [Houicher et al., 2021]. Although it is accelerated by temperature, it also occurs at low storage temperatures (4°C). Therefore, biogenic amine formation, which may continue throughout the cold storage period depending on the type and count of microorganisms, especially due to the activity of biogenic amine-producing psychrophilic bacteria, is an important indicator affecting the quality of the products and a sign of breaking the cold chain during the processing and storage stages of foods [Çelebi Sezer et al., 2022]. It is also largely dependent on fish species. Fish with dark-colored muscles (tuna, mackerel, herring, sardines named as scombroid fish) show higher biogenic amine formation compared to white-muscled fish (cod, hake, sea bass, sea bream, trout, salmon) due to a higher histidine level [Prester et al., 2009]. Free histidine levels in the scombroid fish range from 5,000 mg/kg to 20,000 mg/kg, while Atlantic salmon which belongs to the Salmonidae family has 10 to 200 times lower free histidine levels (less than 1000 mg/kg) than the scombroid fish [FAO/WHO, 2018].
Biogenic amines such as histamine, cadaverine and putrescine are used to indicate deterioration. Due to its toxicological effects, histamine is currently the only biogenic amine for which maximum levels have been set in the EU and USA. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (USFDA), food is considered spoilt when the histamine level reaches 50 ppm [FDA, 2005]. Therefore, Codex Alimentarius standard recognizes histamine level as a spoilage and hygiene indicator for fish. According to the EU legislation, the histamine level in fish offered for consumption should not exceed 100 mg/kg for tuna, mackerel and sardines, and 200 mg/kg for cod and salmon [EU, 2013]. In turn, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) stipulated the acceptable level of histamine below 200 mg/kg for chilled and frozen fish [EFSA, 2011].
Modified atmosphere packaging, used for the preservation of seafood to prolong shelf-life by reducing the microbiological growth and retarding the enzymatic degradation, proves to be an effective treatment for slowing down the formation of biogenic amines in salmon [Çelebi Sezer et al., 2022; Qian et al., 2022]. The inhibitory effect of MAP on the formation of bio-genic amines has been associated with the antimicrobial effects of carbon dioxide on decarboxylase producing microorganisms [Çelebi Sezer et al., 2022]. De la Hoz et al. [2000] reported that the biogenic amine levels of salmon fillets packaged in modified atmosphere with CO2 at different rates increased during cold storage. The levels of cadaverine and histamine in CO2-packaged samples were found to be half of those found in the air-packaged samples. The levels of spermine and spermidine remained almost close to the initial values in all packages, while no significant change was observed in phenylethylamine and tryptamine values. Tryptamine recorded for the first time on day 5 of storage was similar to the present study.
A significant correlation was reported between the counts of certain microorganisms and the formation of biogenic amines. Particularly, a positive correlation was found between mesophilic bacteria and tryptamine, putrescine, tyramine and histamine, as well as between psychrophilic bacteria and putrescine, tyramine, tryptamine and spermidine, between Enterobacteriaceae and putrescine, cadaverine and histamine, and between Pseudomonas and putrescine and cadaverine [Arulkumar et al., 2023].
Oxidative changes
The TBARS values that indicated the fatty acid oxidation of salmon fillets are given in Table 3. The gas composition in MAP had a significant effect on lipid oxidation inhibition. The TBARS values of salmon fillets were close to 1 mg MDA/kg in the air-packaged group after 6th day of cold storage, while this value was exceeded on day 24 in the CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP samples. A significant difference was recorded between the air and other packaging conditions during storage (p<0.001). Besides, the difference between samples in O2 containing and non-containing packages was found to be significant (p<0.001), showing the lowest oxidation in CO and 60% CO2 packages.
Table 3
Oxidative changes in salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period.
[i] Composition of gas mixtures used in MAP of different groups of salmon fillets are shown in Table 1. Results are presented as mean ± standard error. Means within a column with different letters (a–e) are significantly different (p<0.05). Means within a row with different letters (A–H) are significantly different (p<0.05). ***, p<0.001; NS, not significant; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid reactive substance; MDA, malondialdehyde; TMA-N, trimethylamine nitrogen; TVB-N, total volatile basic nitrogen; MAP, modified atmosphere packaging.
Amanatidou et al. [2000] stated that TBARS values of salmon increased significantly after 14 days of storage at 5°C. Zhang et al. [2022] emphasized that modified atmosphere packaging effectively inhibited lipid oxidation in seafood fillets and that TBARS values of air-packaged samples increased rapidly after a slow increase on the first days of storage. However, a slow increase was determined in MAP products over the storage period, indicating that the 70% CO2/30% N2 gas mixture most effectively inhibited lipid oxidation. Also, it was highlighted that the increase in CO2 resulted in lower TBARS values, probably due to limited microbial growth and release of lipolytic enzyme. Similarly, in the present study, higher O2 concentrations led to an increase in TBARS value, while increasing CO2 levels in the package reduced the formation of oxidative compounds.
The TBARS value is an efficient indicator of rancidity and is widely used to determine the degree of fatty acid oxidation of seafood [Bulut et al., 2023]. While in some studies TBARS levels of less than 5 mg MDA/kg are considered to be the threshold for good quality, the maximum acceptable limit for chilled fish intended for human consumption is approved at 8 mg MDA/kg [Secci & Parisi, 2016]. In the present study, TBARS value reached 1.17 and 1.20 mg MDA/kg in the salmon samples packaged in the modified atmosphere containing CO and high CO2, while 2.40 mg MDA/kg was determined in the air-packaged samples at the end of storage (Table 3).
The TMA-N values of salmon fillets showed an increase in all packages parallel to the deterioration process throughout the storage time (Table 3). This increase was greater in the samples packaged with ambient air than in the modified atmosphere-packaged samples, while a relatively slower rise was observed in the 60% CO2-MAP ones. The TMA-N value obtained on the last day of storage in the air-packaged samples reached 23.02 mg/100 g and differed significantly compared to MA-packages, whereas salmon samples packaged in CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP did not exceed 10 mg/100 g on the 27th day of storage, while those packaged in high O2 exceeded 10 mg/100 g after 21 days (p<0.001).
The most widely used chemical parameters for determining the quality of fish and fishery products are TMA-N and TVB-N. The TMA-N value indicates the reduction in trimethylamine oxide due to the activity of spoilage organisms. Besides, this value also includes trimethylamine (formed by spoilage bacteria), dimethylamine (formed by autolytic enzymes), ammonia (formed by deamination of amino acids) and other volatile nitrogenous compounds related to spoilage [Fuentes-Amaya et al., 2016]. Although it varies for fish species, TMA-N value of 10–15 mg/100 g is the limit of acceptability and spoilage, while it is below 2 mg/100 g in very fresh fish [Summers et al., 2017].
The TVB-N values of salmon fillets increased in all packaging groups throughout the storage time (Table 3). A significant (p<0.001) difference was observed in TVB-N values between the air-packaged and modified atmosphere-packaged salmon. Especially the TVB-N levels of salmon fillets packaged with ambient air showed a faster increase compared to the other packages, and also the fillets showed signs of deterioration by exceeding 30 mg N/100 g on the 12th day. TVB-N values of these samples were recorded as 50.40 mg N/100 g on the last day of storage. Salmon packaged with CO and 60% CO2 exceeded 30 mg N/100 g only after the 24th day of storage.
TVB-N are the total nitrogen compounds including ammonia, amines and other alkaline nitrogenous substances formed as a result of protein degradation during the storage process in seafood [Zhang et al., 2022]. Thus, the TVB-N value determines volatile nitrogen formed in the products [Fuentes-Amaya et al., 2016]. The increase in the level of nitrogenous compounds with the progression of spoilage in seafood is an important criterion in determining its shelf-life. In the seafood quality classification based on TVB-N values, up to 25 mg N/100 g denotes high quality, up to 30 mg N/100 g indicates good quality, up to 35 mg N/100 g denotes acceptable food and above 35 mg N/100 g is considered as spoilt [Fuentes-Amaya et al., 2016]. Maximum limits for TVB-N content depending on the fish species are provided as 25–35 mg N/100 g in the EU Regulation 1022/2008 [Esteves et al., 2021].
Fletcher et al. [2002] determined that TVB-N values of salmon remaining below 20 mg N/100 g for 90 days in MAP containing various level of CO2 (10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80 and 100 cm3) at 0°C, whereas high CO2 concentrations caused a decrease in the salmon overall quality. De la Hoz et al. [2000] reported that the TVB-N value of salmon fillets remained stable (<5 mg N/100 g) until the 9th day in all packages, while a significant increase in its values was observed especially in air-packaged salmon fillets that reached to 20 mg N/100 g at the end of storage. Moreover, it was noted that the initial TVB-N values could be maintained for 11 days in the salmon fillets packaged with CO2. Similarly, Kritikos et al. [2020] reported that the TVB-N values of salmon slices did not reach the regulatory limit of 30–35 mg N/100 g at the end of 11 days shelf-life. Furthermore, in the present study, salmon fillets packaged with CO and high concentration of CO2 exceeded 20 mg N/100 g only after the 12th day of storage. In addition, Zhang et al. [2022] emphasized that the greater increase in TVB-N values of fish was observed in air-packing compared to MAP. This was mainly due to the higher CO2 content in MAP, which delayed bacterial activity and chemical reactions [Sivertsvik et al., 2003]. The changes observed in TVB-N values of modified atmosphere-packaged salmon under cold storage were consistent with the results obtained from bacterial counts of fish [Qian et al., 2022]. Additionally, modified atmosphere packaging has been proved effective in delaying protein degradation regardless of gas composition and can be used to extend the shelf-life of fish that plays an effective role in keeping TVB-N levels below consumable limits (approximately 20 mg N/100 g) [Bulut et al., 2023].
Instrumental color evaluation
The color parameters (CIE L*, a*, b*) and total color difference (ΔE) of salmon fillets stored under modified atmospheres and air during the cold storage for 27 days are given in Table 4. A significant difference was observed in the lightness values of salmon fillets throughout the storage time between air-packaged and MAP-packaged samples (p<0.001). The L* values of salmon stored under MAP increased during the first 9 days of storage and then showed a decreasing trend until the end of storage. The L* value of the air-packaged samples was almost constant during entire storage, while the values recorded for high CO2 and CO containing packages were lower than those determined for the air-packaged ones. The increase in the L* values may be explained by denaturation of protein and the difference in reflective properties due to drip loss on fillet surfaces [Chan et al., 2021b].
Table 4
Instrumental color parameters of salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period.
[i] Composition of gas mixtures used in MAP of different groups of salmon fillets are shown in Table 1. Means within a column with different letters (a–f) are significantly different (p<0.05). Means within a row with different letters (A–H) are significantly different (p<0.05). ***, p<0.001; NS, not significant; SE, standard error; L*, lightness; a*, redness; b*, yellowness; ΔE, total color difference; MAP, modified atmosphere packaging.
There was a significant decrease in the redness values of air-packaged salmon during storage period (p<0.001), while bright red color was retained in CO-MAP and 40% CO2-MAP. However, 60% CO2 in the package atmosphere caused a decrease in the stability of red color. The yellowness values of salmon showed a decrease throughout storage time in packages containing air and 10–20% O2, while the changes in b* values increased until the 18th day of storage in MA-packages containing 40% CO2 gas mixture, and then slightly decreased until the end of storage. Also, a constant change was recorded in CO-MAP during the same period. The losing of redness and yellowness value in salmon fillets may also be associated with an increase in protein denaturation and drip loss during storage, independent of the packaging method. Additionally, the higher ΔE in salmon fillets was generally recorded in the O2-MAP groups during 27-day cold storage. However, the smallest color change was observed in CO-MAP until 21st day of storage, while salmon packaged with 40% CO2 remained stable in this respect during entire storage.
Chan et al. [2021b] reported that the packaging of salmon fillets with 60% CO2 resulted in a decrease the redness and yellowness values during storage period, which is in line with our findings. The decline in redness and yellowness values of salmon fillets was associated with the increase in protein denaturation and drip loss during storage, regardless of the packaging method.
Sensory evaluation
The sensory evaluation (appearance, color intensity, off-odor, tenderness) scores of salmon fillets during the cold storage for 27 days are given in Table 5. The sensorial properties of the air-packaged samples remained within acceptable limits only until the 15th day. However, the changes in their chemical and microbial parameters after this period showed that they were consumable for only one week in cold storage. Furthermore, it was revealed by sensory evaluations that the shelf-life of salmon fillets can exceed 2 weeks when packaged with CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP.
Table 5
Sensorial properties of salmon fillets packaged in air and modified atmosphere during storage period.
[i] Composition of gas mixtures used in MAP of different groups of salmon fillets are shown in Table 1. Means within a column with different letters (a–d) are significantly different (p<0.05). ***, p<0.001; NS, not significant; SE, standard error.
The tenderness scores of cold-stored salmon samples showed similar changes within the groups until the 15th day of storage. As a result of microbial and chemical changes occurring in salmon samples over time, there was a loss in the tenderness of the samples belonging to all groups. At the end of the 27-day storage period, although the tenderness scores of the samples stored in CO-MAP and 60% CO2-MAP were found to be higher, no significant difference was detected between them and the other groups. Salmon fillets packaged with CO and CO2/N2 gas mixtures remained within the consumable limits in terms of odor and color characteristics until the end of the storage period, while their appearance characteristics changed in parallel with structural alteration.
Preservation techniques are industrially utilized ways to ensure both food safety and the sensory appeal of fresh salmon. Thus, the packaging methods for seafood have evolved with the use of modified atmosphere packaging [Merlo et al., 2019]. The CO2 used in MAP suppresses microbial growth by prolonging the lag phase and reducing the accumulation of hypoxanthine and volatile bases, i.e., compounds responsible for spoilage. This minimizes the formation of unpleasant odors in salmon [Chan et al., 2021b]. Similar with the present study, salmon fillets packaged with 75% CO2/25% N2 gas mixture maintained acceptable sensory properties for 27 days of storage, while total bacterial loads exceeded 106 CFU/g after 18 days. Furthermore, increasing the CO2 concentration to 90% enabled the product to remain acceptable in terms of sensory properties for up to 28 days [Fernandez et al., 2009].
Despite the increasing count of Pseudomonas, there was minimal organoleptic change in salmon fillets after 30 days with no negative change in structure or odor. The off-odor caused by trimethylamine and sulfhydryl and the bitter taste due to the increase in hypoxanthine are responsible for the microbial spoilage by Pseudomonas spp. [Milne & Powell, 2014]. In addition, degradation products formed by spoilage microorganisms, such as Hafnia alvei, Photobacterium phosphoreum and Carnobacterium maltaromaticum, are also responsible for the undesirable odors of salmon under MAP [Macé et al., 2013].
CONCLUSIONS
The findings of this study confirmed that MAP with 60% CO2 and 0.4% CO could be an alternative means for extending cold storage of salmon fillets at 1°C. Selecting appropriate gas combinations in the packaging of fresh salmon under modified atmosphere provides extended shelf-life while maintaining the quality parameters of the product by preventing oxidation, maintaining color stability, retarding microbial growth and improving sensory properties. Consequently, modified atmosphere packaging under high concentrations (60–50%) of CO2 or low level of CO (0.4%) was determined as an effective treatment in extending the shelf-life of salmon and other fatty fish species by preserving their quality characteristics.

