INTRODUCTION
Copper is one of the most important trace elements, essential for both humans and animals to ensure that life processes occur harmoniously, maintaining a state of homeostasis [Malavolta et al., 2015]. The main sources of Cu include food, drinking water, and Cu-containing supplements [Herman et al., 2022; Olivares & Uauy, 1996]. Sources of copper in food can be both inorganic and organic, with the latter being considered more bioavailable and having higher retention in the body [Jankowski et al., 2020]. However, comparative results of organic vs. inorganic Cu sources are inconsistent. In recent years, researchers have focused on copper nanoparticles (Cu-NP) as an alternative to the aforementioned sources, due to the unique physical and biological properties of nanometals, including bioavailability, which may limit excessive copper excretion in feces and urine. Some authors suggest that Cu-NP in the body may play the same role as copper from conventional sources, while still allowing for reduced supplementation options [Kiyani et al., 2022]. But, in our opinion, the truth about the dietary Cu-NP should be rediscovered. In the first years of the current century, the results regarding Cu-NP application as an alternative feed component were rather rare. Gonzales-Eguia et al. [2009] demonstrated enhanced production parameters of piglets fed a diet with Cu-NP supplementation. On the other hand, Pineda et al. [2013] showed disrupted development of internal organs in chicken embryos. The Cu-NP has more and more applications in daily life these days. They are utilized in the manufacturing of chips, power sources, gas detectors, photovoltaic generators, electronic devices, and heating systems [Zhang et al., 2023]. Cu-NP have been used at a growing rate in the manufacturing of medications and beauty products because of their strong bactericidal characteristics [Anreddy, 2018; Ermini & Voliani, 2021]. Cu-NP are also proposed by some researchers as a potential dietary supplement for consumers struggling with mineral deficiencies in the body [Baravkar et al., 2021; Kargin et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2016].
There is no doubt that adjusting the dietary fiber content and fiber type may, directly and indirectly, affect copper bioavailability by modifying its absorption and modulating the bioavailability of mineral antagonists. Studies indicate that soluble fiber is beneficial, which, in addition to increasing the bioavailability of copper, favorably modulates the passage of digestive contents in the gut [Baye et al., 2017]. Different dietary fibers substantially affect the large intestinal pH values, dry matter content, buffering capacity of digesta, and finally the microbial community actions in the large gut lumen [Perler et al., 2023]. The impact of consumed nanoparticles in the body, including on bacteria colonizing the large intestine, is usually described as a double-edged sword effect that both benefits and harms. This rule appears to apply to the interaction between gut microbes and Cu-NP. Our previous studies have shown that the addition of Cu-NP to the cellulose-containing diet of rats resulted in reduced proliferation of the cecal microbiota and lower bacterial enzymatic activity, leading to a diminished amount of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced [Cholewińska et al., 2018]. Strychalski et al. [2021] showed the modulatory effect of dietary fiber type on the enzyme release rate from bacterial cells, thus creating a large intestinal environment with higher or lower extracellular enzyme activity.
Considering that fiber is an essential dietary component and that its type would be critical to the absorption and subsequent physiological action of Cu-NP, the present study aimed to verify the hypothesis that the effect of Cu-NP on the metabolic status of the fecal microbial community is strongly reliant on the physiological function of different dietary fiber types. In the present study, it has been proposed that a dietary concomitant presence of Cu-NP with either a control inert (cellulose) or a prebiotic (inulin) or a viscous (pectin) or a bulking (psyllium) fiber would significantly and in a different way alter the enzymatic activity of the bacteria and the synthesis of short-chain fatty acids in the rat feces.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Nanoparticles and fiber source
Copper nanoparticles (Cu-NP) were purchased at Sky Spring Nanomaterials Incorporation (Houston, TX, USA). The characteristics of the Cu-NP preparation were as follows: spherical morphology, powder with 99.9% purity, particle size of 40–60 nm, specific surface area of 12 m2/g, bulk density of 0.19 g/mL, and true density of 8.9 g/mL. In the diets prepared in our laboratory (Institute of Animal Reproduction and Food Research of the Polish Academy of Sciences, Olsztyn, Poland), α-cellulose (Sigma, Poznań, Poland) was used as control fiber, whereas inulin (FrutafitTex, Sensus, the Netherlands), pectin (PectinE 440(I), Brouwland, Beverlo, Belgium), and psyllium (Psyllium husk powder, NaturaleBio, Rome, Italy) were used as fibers with different functional properties.
The in vivo protocol
The animal study was conducted on 100 nine-week-old outbred male Wistar rats (Cmdb:Wi) fed diets with two Cu-NP contents (recommended 6.5 mg/kg (L) and two-times higher (H)) along with different dietary fibers (cellulose, inulin, psyllium, pectin; see Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials). The rats were randomly assigned to ten study groups, with 10 animals in each group. The experimental group schema was as follows: Control C and CH groups, fed a control diet containing CuCO3 of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg and 8% of cellulose (n=10 per group); groups CN and CNH, fed diets with L and H content of Cu-NP, respectively, and 8% of cellulose; groups PN and PNH, fed diets with L and H content of Cu-NP, respectively, 2% of cellulose and 6% of pectin; groups JN and JNH, fed diets with L and H content of Cu-NP, respectively, 2% of cellulose and 6% of inulin; groups SN and SNH, fed diets with L and H content of Cu-NP, respectively, 2% of cellulose and 6% of psyllium. The Local Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments in Olsztyn (Poland) approved the experimental protocol (No. 19/2021). The environment in the animal room was characterized by a stable temperature (22±1°C), relative humidity of 60±5%, a 12-h light-dark cycle, and a ventilation rate of 15 air changes per hour. The experiment lasted 6 weeks, and the animals had unlimited access to diet and water. The nutritional acclimation period on diet C was 5 days for all rats (see Table 1 for diet compositions).
Table 1
The composition (%) of control diets with CuCO3 at two levels (C and CH) and experimental diets with Cu nanoparticles (Cu-NP) at two levels (CN and CNH), and with Cu-NPs and replacing part of celulose with pectin (PN and PNH), inulin (JN and JNH) and psyllium (SN and SNH).
| Component | C/CH | CN/CNH | PN/PNH | JN/JNH | SN/SNH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Casein1 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 |
| dl-methionine | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Cellulose | 8.0 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Pectin | – | – | 6 | – | – |
| Inulin | – | – | – | 6 | – |
| Psyllium | – | – | – | – | 6 |
| Choline chloride | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Rapeseed oil | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 |
| Cholesterol | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Vitamin mix2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Mineral mix3 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Maize starch4 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 64.0 |
| Cu source | |||||
| CuCO3 (mg/kg diet) | 6.5/13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cu-NP (mg/kg diet) | 0 | 6.5/13 | 6.5/13 | 6.5/13 | 6.5/13 |
2 AIN-93G-VM, g/kg mix: 3.0 nicotinic acid, 1.6 Ca pantothenate, 0.7 pyridoxine-HCl, 0.6 thiamin-HCl, 0.6 riboflavin, 0.2 folic acid, 0.02 biotin, 2.5 vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin, 0.1% in mannitol), 15.0 vitamin E (all-rac-α-tocopheryl acetate, 500 IU/g), 0.8 vitamin A (all-trans-retinyl palmitate, 500,000 IU/g), 0.25 vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol, 400,000 IU/g), 0.075 vitamin K1 (phylloquinone), 974.655 powdered sucrose.
Sample collection and analyses
The fecal samples were collected on days 0, 1, 2, 7, 14, 21, and 42. The fecal pH was measured just after sample collection (pH meter, Model 301, Hanna Instruments, Vila do Conde, Portugal). The details of detreminations of the fecal ammonia, SCFA content and bacterial enzyme (α- and β-glucosidase, β-glucuronidase, α-arabinofuranosidase) activity were provided elsewhere [Gugołek et al., 2021]. In brief, ammonia released from fresh feces was difuded to boric acid solution in Conway’s dishes and detremined by titration with sulfuric acid. Results were expressed in mg/g.
Gas chromatography method was used to determine the SCFA content in fecal digesta. The separation of SCFA was carried out on a SGE BP21capillary column (30 m × 0.53 mm, Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA) connected to the Shimadzu GC-2010 chromatograph with a flame ionization detector (Kyoto, Japan). Initial column temperature was 85°C and it was finally raised to 180°C at the rate of 8°C/min. Temperatures of the detector and the injector were maintained at 180°C and 85°C, respectively. Identification of individual SCFA in the samples was performed comparing the retention times of their peaks with those of standards, including acetic, propionic, butyric, iso-butyric, iso-valeric, and valeric acids, which were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Quantitative evaluation was performed based on the generated standard curves. Content of SCFA in fecal digesta was expressed in μmol/g.
The appropriate p-nitrophenol glycosides were used as substrates to determine the α-glucosidase, β-glucosidase, β-glucuronidase, and α-arabinofuranosidase activities in fecal digesta. These were p-nitrophenyl-α-d-glucopyranoside, p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside, p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucuronide, and p-nitrophenyl-α-l-arabinofuranoside, respectively. p-Nitrophenol released from the substrates was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the reaction mixture at 400 nm. The enzymatic activity was expressed as μmol p-nitrophenol released per h per g of feces. The total enzymatic activity was assessed after bacterial cell lysis of fecal contents by homogenization with glass beads (diameter of 212–300 μm) in ice using the FastPrep®-24 system (MP Biomedicals, St. Ana, CA, US). Fecal digesta samples were not homogenized for extracellular enzymatic activity determination. Values of the intracellular enzyme activity were calculated based on the difference.
Statistical analysis
The data were subjected to two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Student’s t-test. A single experimental group (CN, PN, JN, SN) was compared with the control C group using the t-test. Similarly, the CNH, PNH, JNH, SNH groups were compared with the aid of the t-test with the control CH group. Two-way ANOVA (all groups treated with copper nanoparticles: CN, CNH, PN, PNH, JN, JNH, SN, SNH) was applied to assess the effects of two main factors: D – the dose of added Cu-NP (L, 6.5 mg/kg and H, 13 mg/kg) and F – dietary fiber type (cellulose, pectin, inulin and psyllium) as well as the D×F interaction. The Duncan’s multiple range test was used to assess means when ANOVA revealed significant treatment effects. Before performing any statistical analysis, the data were examined for normality of distribution. Differences with p<0.05 were considered significant (Statistica 12.0; StatSoft Corp., Kraków, Poland).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A number of in vivo studies have demonstrated an important role of the content of standard dietary sources of copper in modulating the large gut microbiota profile [Cheng et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019], and even a stronger effect of the dietary inclusion of copper nanoparticles on the composition and activity of the intestinal microbial community [Cholewińska et al., 2018; Lai et al., 2022]. Bacteriological screenings (for example, identifying specific bacterial taxa) are important for defining the gut environment, but they are restricted in their usefulness to studies of organism metabolism, nutrition, and health condition [Bankier et al., 2018; Utembe et al., 2022]. An alternative approach is to use biochemical assays to assess the functional activity of the entire microbiome. Their findings could help understand the contribution of the community of microbes in gut metabolism. Previous research conducted by our team endeavored to assess the amount and composition of the microbial digestion end products (ammonia, SCFAs) along with the activity of particular bacterial enzymes in the large intestine digesta, in the latter case, instead of the bacterial count [Gugołek et al., 2021].
The two-way ANOVA showed that, irrespective of Cu-NP dietary application, the functional fiber (pectin, inulin, psyllium) addition to a diet enhanced the extracellular activity of fecal bacterial α-glucosidase on day 1 as compared to the cellulose treatment (main fiber effect in the two-way ANOVA; Figure 1A). The D×F interaction indicated the highest extracellular activity of that enzyme on day 2 in groups PN and SN while on day 7 – in groups PN, JN, and SN. On the next subsequent days 14, 21, 42, the highest extracellular activity of fecal α-glucosidase was determined in the rats fed a diet with psyllium and a lower one when feeding animal a diet with Cu nanoparticles at 6.5 mg/kg diet. During all days analyzed between day 2 and 42, the lowest extracellular activity was found in the CN and CNH groups, with the reduction in activity on days 21 and 42 being most pronounced in the latter group (p<0.05 vs. all other groups). In the aforementioned time interval (days 2–42), the addition of the higher dose of nanoparticles to the diet resulted in suppressed activity in the functional fibre-fed groups. The exception were the groups fed with inulin (JN and JNH) where extracellular activities of α-glucosidase in the feces were similar on day 2 and day 42. On days 2, 7, 14, 21, and 42, the t-test showed significantly lower activity of fecal extracellular α-glucosidase in the Cu-NP groups fed diets containing cellulose as compared to their CuCO3 control counterparts (CN vs. C and CNH vs. CH). In the case of diets containing functional fibers, the t-test showed an increase in this activity regardless of nanoparticle dose compared to control cellulose diets without copper nanoparticles. The exception was the JNH group, whose feces showed higher extracellular α-glucosidase activity compared to the CH group only in the last measurement, i.e., on day 42. Regardless of fiber type, the dietary addition of the higher Cu-NP dose significantly diminished the intracellular activity of bacterial α-glucosidase in the rat feces on days 1, 2, and 7 (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). Two-way ANOVA showed that all three functional fibers enhanced that activity on those days as compared to cellulose, irrespective of Cu-NP dose. The significant D×F interaction noted on days 14, 21, and 42 revealed the highest intracellular activity in the JN and SN groups (p<0.05), and the lowest one - in the CN and CNH groups. During all measurement days (period 1–42), the CN and CNH groups showed lower intracellular activity of bacterial fecal α-glucosidase compared to the C and CH groups, respectively (t-test). On days 14, 21, and 42, all the fiber-fed groups showed significantly suppressed intracellular activity of bacterial α-glucosidase in the feces as compared to the respective control groups C or CH. The significant effects (p<0.05) of both fiber type and Cu-NP content in diets on the total fecal α-glucosidase activity on days 1 and 2 were shown by two-way ANOVA (Table S2 in Supplementary Materials). Irrespective of fiber type, a lower total α-glucosidase activity was found in the treatments with the higher dietary dose of Cu-NP. A significant D×F interaction revealed the highest total α-glucosidase activity in the feces of PN, JN, and SN rats on day 7 (p<0.05). On the next subsequent days 14, 21, 42, the aforementioned activity was the highest in groups JN and SN. The CN and CNH feces were characterized by significantly lower total activity of bacterial α-glucosidase on days from 2 to 42 as compared to their respective controls (C and CH, respectively; t-test). On those days (2, 7, 14, 21, 42), the feces of rats fed diets with pectin, inulin, psyllium and with the low Cu-NP dose were characterized by significantly enhanced total activity of bacterial α-glucosidase in comparison to the C control (t-test). The two-way ANOVA showed that, irrespective of Cu-NP dose, the treatments with inulin and psyllium caused a significant decrease in the percentage of fecal microbial α-glucosidase release rate on day 1 (p<0.05 vs. cellulose treatment; Figure 1B). On day 14, the release rate of α-glucosidase was significantly lower in the inulin and psyllium treatments than in the cellulose and pectin ones. Regardless of the fiber type, the high Cu-NP dose enhanced the α-glucosidase release rate on day 14 vs. the low nanoparticle dose (p<0.05). A significant D×F interaction noted on days 21 and 42 indicated the highest release rate of that enzyme into the fecal environment in the CN group and the lowest one in the JN animals. On day 7, there was a comparable situation, with the highest release rate being noted in the CNH rat feces.
Figure 1
Extracellular microbial activity of α-glucosidase (A) and β-glucosidase (C) in the feces of rats during the feeding period as well as the release rate of α-glucosidase (B) and β-glucosidase (D).
The dietary treatments: groups C and CH, fed a control diet with standard and enhanced Cu content from CuCO3 (6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively) and 8% cellulose; groups CN and CNH, fed diets with Cu-nanoparticles (Cu-NP) content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, and 8% cellulose; groups PN and PNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% pectin; groups JN and JNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% inulin; groups SN and SNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% psyllium. Significant differences (p<0.05) between groups for an individual treatment time are marked with different letters (a–e) shown above the graph (the color of the points on the curve corresponds to the color of the letters). They are indicated only in the case of a significant interaction D×F (p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 6.5 mg/kg (CN, PN, JN, SN) and the control C are indicated by # (t-test, p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 13 mg/kg (CNH, PNH, JNH, SNH) and the control CH are indicated by & (t-test, p<0.05).
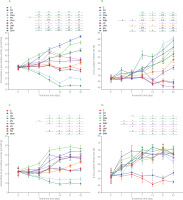
The two-way ANOVA indicated that, regardless the Cu-NP addition, the highest activity of bacterial extracellular β-glucosidase was recorded since day 1 till 42 in feces of the rats fed the diet with pectin (Figure 1C). Irrespective of the fiber type, the effect of Cu-NP content in diet on extracellular β-glucosidase activity on days 2-42 was significant (p<0.05); the high Cu-NP content caused a lower enzyme activity. As compared via the t-test with their respective control groups, the CN and CHN feces were characterized by significantly diminished extracellular β-glucosidase activity on days 7, 14, 21, and 42. All pectin, inulin and psyllium groups showed higher extracellular β-glucosidase activity on days 21 and 42 as compared to their respective controls (t-test). Regardless of the Cu-NP addition, the “functional fiber” treatments enhanced the intracellular activity of fecal bacterial β-glucosidase compared to the cellulose treatment from the second measuring day (p<0.05) except day 2 for the pectin treatment (Table S3 in Supplementary Materials). This enzyme activity was decreased by the high Cu-NP dose vs. the low dose on days 7, 14, 21, and 42, irrespective of dietary fiber type. On day 2, the t-test showed suppressed intracellular activity of fecal bacterial β-glucosidase in the CN, CNH, and PNH groups (p<0.05 vs. respective controls C and CH). On the subsequent days, that activity in all groups fed diets with Cu-NP was diminished vs. respective controls fed diets with CuCO3 (t-test). From day 2, all “functional fiber” treatments significantly increased (p<0.05) the total activity of fecal β-glucosidase compared to cellulose treatment, irrespective of Cu-NP addition (Table S4 in Supplementary Materials). Regardless of the fiber type, the higher Cu-NP content in diet caused a significantly lower total β-glucosidase activity in the rat feces on all measuring days, except day 0 and 1 (p<0.05). The two-way ANOVA showed that, regardless of the dietary Cu-NP dose, the addition of pectin to a diet containing copper nanoparticles caused a significant increase in the fecal microbial β-glucosidase release rate on day 1 (p<0.05 vs. cellulose; Figure 1D). The t-test showed that from day 7 all feces of the rats from groups fed diets with Cu-NP showed an increased percentage of β-glucosidase release rate in comparison to the respective controls C or CH (p<0.05).
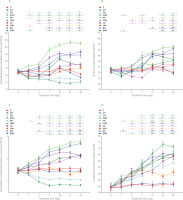
Regardless the fiber type, the higher content of Cu-NP in diets resulted in diminished extracellular activity of bacterial β-glucuronidase on days 1, 2, 14, and 21 (Figure 2A). On those days, the pectin dietary addition caused the highest enzyme activity, irrespective of Cu-NP dose (p<0.05). A significant D×F interaction was noted on days 7 and 42, and the nature of that interaction revealed the highest extracellular β-glucuronidase in the PN feces (p<0.05 vs. all other groups). The t-test showed that from day 1 till the end of experiment the CN and CNH feces were characterized with a significantly lower extracellular activity of bacterial β-glucuronidase in comparison to their respective controls C and CH (p<0.05). The dietary treatments with pectin, inulin and psyllium caused a significant increase in intracellular fecal activity of β-glucuronidase vs. cellulose on day 1, regardless of the Cu-NPs dose (Table S5 in Supplementary Materials). On the subsequent measuring days, a significant D×F interaction was noted and its nature indicated the highest intracellular β-glucuronidase activity upon rat feeding a diet with inulin and the lower dose of copper nanoparticles. The t-test showed that CN and CNH groups had significantly lowered activity of intracellular β-glucuronidase from day 2 till the end of experiment (p<0.05 vs. C and CH, respectively). On days 14, 21, 42, such a situation was also observed in the pectin and psyllium groups (except PNH vs. CH on day 21). All treatments with “functional fiber” enhanced the total activity of fecal bacterial β-glucuronidase on day 1 vs. cellulose, irrespective of Cu-NP dose (Table S6 in Supplementary Materials). Regardless of the fiber type, the high Cu-NP dose in a diet decreased that activity vs. L dose (p<0.05). A significant D×F interaction noted on measuring days 2, 7, 14, 21, 42 revealed the highest and the lowest total activity of fecal bacterial β-glucuronidase in the PN and CNH groups, respectively. Generally, the t-test showed that total β-glucuronidase activity in the feces of both pectin groups (PN and PNH) was significantly higher than in C and CH controls on all measuring days. The percentage of β-glucuronidase release rate was significantly decreased by the higher Cu-NP dose, irrespective of the fiber type (p<0.05 vs. low dose; Figure 2B). The two-way ANOVA showed that, regardless of Cu-NP dose, the fiber pectin treatment caused the highest fecal β-glucuronidase release rate on days 1, 2, and 7 (p<0.05 other fibers). On day 14, the pectin and psyllium treatments increased the β-glucuronidase release rate in comparison to the cellulose and inulin treatments. A significant D×F interaction recorded on days 21 and 42 showed the highest and the lowest β-glucuronidase release rate in the PN and CN groups, respectively. The t-test showed that on day 42 all groups, except the CN, showed an increased percentage of β-glucuronidase release rate concerning their controls without Cu-NP. The two-way ANOVA showed that, regardless of the Cu-NP dose, the treatments with pectin and psyllium significantly enhanced the extracellular activity of fecal bacterial α-arabinofuranosidase on day 1 as compared to the cellulose and inulin treatments (p<0.05; Figure 2C). On the subsequent measuring days, i.e., days 2, 7, and 14, the highest and the lowest activity of this enzyme were noted in the pectin and cellulose treatments, respectively. On those days, the higher Cu-NP dose increased extracellular activity of α-arabinofuranosidase in the feces vs. the low nanoparticle dose, irrespective of dietary fiber type. On days 21 and 42, a significant D×F interaction revealed that the PN feces showed the highest extracellular activity of bacterial α-arabinofuranosidase and that the CNH feces showed the lowest ones. The t-test showed that on day 7 and subsequent measuring days, the CN and CNH diets caused a decrease, while remaining dietary treatments (except JN) caused an increase in fecal bacterial α-arabinofuranosidase activity in comparison to the respective controls without nanoparticle application, i.e., C and CH (p<0.05). The two-way ANOVA showed that, regardless of the Cu-NP dose, the pectin and psyllium dietary addition increased intracellular α-arabinofuranosidase activity on day 1 as compared to the cellulose treatments (p<0.05; Table S7 in Supplementary Materials). On days 2, 7, and 14, the pectin, inulin and psyllium treatments excelled the control cellulose one in this respect. A significant D×F interaction revealed the lowest activity of fecal intracellular α-arabinofuranosidase in the CNH rats on days 21 and 42 (p<0.05 vs. all remaining groups). As indicated Table S8 in Supplementary Materials, regardless of the Cu-NP dose, the total activity of fecal bacterial α-arabinofuranosidase was significantly enhanced by pectin and psyllium treatments on day 1 (p<0.05 vs. cellulose and inulin), while on days 2, 7, 14, 21 all three functional fiber treatments excelled the cellulose one in this respect (p<0.05). A D×F interaction noted on day 42 showed the lowest and the highest total α-arabinofuranosidase activity in the CNH and PN, SN groups, respectively (in both cases p<0.05 vs. all other groups). The t-test revealed that on all measuring days, the CN, CNH, and JNH groups showed suppressed total α-arabinofuranosidase activity as compared to respective C and CH controls. A significant D×F interaction noted on days 14, 21, 42 showed the highest and the lowest release rate of bacterial fecal α-arabinofuranosidase in the CNH and JNH groups, respectively (Figure 2D). Interestingly, on those days, the CN group showed significantly lower release rate of that enzyme as compared to the CNH one. In the “functional” fiber counterparts, such a situation was noted on days 21 and 42 between groups JN and JNH (p<0.05). The t-test revealed that from day 7 till the end of the experiment all groups fed diets with copper nanoparticles were characterized with significantly enhanced fecal α-arabinofuranosidase release rate vs. respective controls, i.e., C and CH (p<0.05).
Figure 2
Extracellular microbial activity of β-glucuronidase (A) and α-arabinofuranosidase (C) in the feces of rats during the feeding period as well as the release rate of β-glucuronidase (B) and α-arabinofuranosidase (D).
The dietary treatments: groups C and CH, fed a control diet with standard and enhanced Cu content from CuCO3 (6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively) and 8% cellulose; groups CN and CNH, fed diets with Cu-nanoparticles (Cu-NP) contnet of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, and 8% cellulose; groups PN and PNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% pectin; groups JN and JNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% inulin; groups SN and SNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% psyllium. Significant differences (p<0.05) between groups for an individual treatment time are marked with different letters (a–e) shown above the graph (the color of the points on the curve corresponds to the color of the letters). They are indicated only in the case of a significant interaction D×F (p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 6.5 mg/kg (CN, PN, JN, SN) and the control C are indicated by # (t-test, p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 13 mg/kg (CNH, PNH, JNH, SNH) and the control CH are indicated by & (t-test, p<0.05).
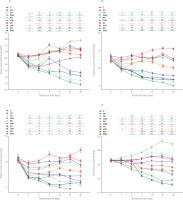
The fecal acetic acid content on day 1 was significantly diminished by the higher Cu-NP dose as compared to the low Cu-NP dose, regardless of the fiber type (Figure 3A). On the subsequent measuring days, a significant D×F interaction was noted with regard to fecal acetic acid. On days 2, 7, 14, and 42, the lowest acetic acid content was determined in the CNH rat feces, while on Day 21 – in the CN and CNH rat feces (p<0.05 vs. all remaining groups). The highest acetic acid content in the feces was noted on day 2 in the feces of the PN and JN rats, on day 7 – in those of JN rats, on day 14 – in those of PN, JN and JNH rats, and on days 21 and 42 – in those of the PN animals (in all cases p<0.05 vs. other groups). The t-test revealed decreased acetic acid content on days 1 and 2 in all experimental groups, except JN as compared to respective C and CH controls (p<0.05). On the subsequent measuring days, such a decrease was noted in the CN, CNH, PNH, SN, and SNH groups (p<0.05 vs. respective C or CH). On day 1, the fecal concentration of propionic acid was diminished by the higher Cu-NP dose, irrespective of fiber type (p<0.05 vs. L dose; Figure 3B). A D×F interaction showed that from day 2 till the end of the experiment the highest and the lowest propionic acid fecal content followed the dietary treatments with JN and CNH diets, respectively (in both cases p<0.05 vs. all other groups). The t-test revealed that the JN feces were the only ones attributed with significantly enhanced propionic acid fecal content vs. C group on days 14, 21, and 42 (p<0.05). The decreased fecal butyric acid content followed the higher Cu-NP dietary dose treatment vs. the low dose on days 1, 2, 7, and 14, regardless of the fiber type (p<0.05; Figure 3C). On day 2, the inulin treatment excelled the other fiber treatments with regard to butyric acid content, irrespective of Cu-NP dose. On day 7, such an increase in butyric acid content was noted in the pectin and inulin treatments as compared to the cellulose and psyllium ones. On day 14, the lowest and the highest butyric acid fecal content were determined in the cellulose and inulin treatments, respectively (in both cases p<0.05 vs. remaining fiber treatments). A significant D×F interaction noted on days 21 and 42 showed the lowest and the highest butyric acid content in the feces in the CNH and JN groups, respectively. The t-test revealed that all groups with dietary addition of copper nanoparticles had lowered butyric acid content in the feces vs. respective C and CH controls, except group JN on days 1, 14, 21, and 42. Additionally, on day 42, the JN feces were characterized with enhanced butyric acid content vs. group C (t-test).
Figure 3
The content of acetic acid (A), propionic acid (B), butyric acid (C) and ammonia (D) in the feces of rats during the feeding period.
The dietary treatments: groups C and CH, fed a control diet with standard and enhanced Cu content from CuCO3 (6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively) and 8% cellulose; groups CN and CNH, fed diets with Cu-nanoparticles (Cu-NP) content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, and 8% cellulose; groups PN and PNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% pectin; groups JN and JNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% inulin; groups SN and SNH, fed diets with Cu-NP content of 6.5 and 13 mg/kg from, respectively, 2% cellulose and 6% psyllium. Significant differences (p<0.05) between groups for an individual treatment time are marked with different letters (a–e) shown above the graph (the color of the points on the curve corresponds to the color of the letters). They are indicated only in the case of a significant interaction D×F (p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 6.5 mg/kg (CN, PN, JN, SN) and the control C are indicated by # (t-test, p<0.05). Significant differences between each group fed diet with Cu-NP content of 13 mg/kg (CNH, PNH, JNH, SNH) and the control CH are indicated by & (t-test, p<0.05).
An enhanced fecal content of putrefactive SCFA followed the pectin dietary addition on days 2 and 7, irrespective of Cu-NP dose (p<0.05 vs. remaining fiber treatments; Table S9 in Supplementary Materials). On days 21 and 42, the CNH and PN rats had the lowest and the highest putrefactive SCFA content in the feces, respectively. The t-test showed that all experimental Cu-NP groups had lowered fecal putrefactive SCFA as compared to their respective C or CH controls from day 2, except the PN group. The two-way ANOVA showed that on day 1, the higher Cu-NP dose caused a decrease in the total fecal SCFA content, regardless of the fiber type (p<0.05 vs. L dose; Table S10 in Supplementary Materials). From day 2, a significant D×F interaction was noted for fecal total SCFA in all subsequent measuring days. The nature of that interaction indicated the lowest total SCFA level in the CNH group on all measuring days (on day 7 in the SNH group as well) and the highest total SCFA content on days 2 and 7 in the JN feces, on day 14 – in the JN and PN feces, and on days 21 and 42 – in the PN feces (in all cases p<0.05 vs. other groups).
As in our previous experiments with the addition of various nanoparticles to the diet [Cholewińska et al., 2018], dietary Cu-NP used in the present experiment suppressed the activity of most of the analyzed bacterial enzymes in the feces and diminished the amounts of SCFAs produced by the microbiota. As for the effect of the doubled Cu-NP dose, lower levels of enzyme activity and amounts of bacterial metabolites were indeed found, although this was not a doubly suppressive effect. One of the most important results observed was the limiting effect of Cu-NP on extracellular enzymatic activity and greater release of bacterial enzymes into the environment from within the bacterial cells upon the influence of nanoparticles. The extracellular activity of bacterial enzymes has direct implications for the rate at which nutrients and non-nutrients undergo microbial digestion in the large intestine. Extracellular enzyme activity is influenced by the type and counts of bacterial species present in the digesta and by the rate of enzyme secretion by bacterial cells. With regard to the presented hypothesis, a higher release rate of glycoside hydrolases could be an important adaptive mechanism of intestinal bacteria which enables them to acquire additional energy from the large intestine through fermentation in the situation when Cu-NP seem to reduce bacterial activity and probably bacterial count. Doubling the dose of copper nanoparticles added to the diet increased the percentage of enzymes released, although in some cases the increase was not statistically significant, such as for α-glucosidase and β-glucosidase in the last two measurements on days 21 and 42. According to some reports, nanoparticles may reduce the amount of microorganisms by entering bacteria through nanometric holes and disrupting internal organellas [Azam et al., 2012]. Mahapatra et al. [2008] showed diminished effect of nano-CuO on Klebsiella, Salmonella and Shigealla count via damaging intracellular enzymes. Lai et al. [2022] concluded their research that among a broad range of Cu-NP’s properties, their capability for microbial growth inhibition, membrane disruption, DNA damage, and enhancement in oxidative stress in bacteria are of paramount importance when intestinal environment is considered. In the present experiment, the release rate of intracellular enzymes into fecal milieu was not totally enhanced under the higher tested copper nanoparticle dose, indicating selective inhibition of enzymatic activity rather than disruption of the bacterial cell membrane. Copper attached to nanoparticles made from chitosan removed gastrointestinal pathogens such as Salmonella species, but left Lactobacilli and other beneficial commensals unharmed, according to Han et al. [2010] study.
In the present experiment, it was hypothesized that the dietary inclusion of fiber with prebiotic (inulin), viscous (pectin) or bulking (psyllium) properties would alleviate adverse effects of copper nanoparticles on intestinal microbial activity, the latter effect observed in our previous experiments with diets containing cellulose [Cholewińska et al., 2018]. The scientific literature demonstrates that viscous dietary fiber effectively delays and reduces the absorption of nutrients in the intestine [Deehan et al., 2022]. This, of course, causes these nutrients to be transported to the large intestine in greater quantities, and therein used by the microbiota for growth and metabolite production. Żary-Sikorska and co-authors [2016] confirmed in their in vivo study that, compared to prebiotic fructans and less processed fiber-polyphenol preparations, pectin had the greatest viscosity-enhancing properties in the small intestine and was fermented most rapidly, sometimes too vigorously, in the large intestine. At this point, there is little need to elaborate on the well-studied theme of the prebiotic positive effect of inulin-type fibers on the gut microbiota in both a taxa-dependent manner and its metabolic activity [Juśkiewicz et al., 2007]. An interesting case, and therefore not missed in this experiment, is the intestinal behavior of psyllium. Psyllium is a viscous, gel-forming fiber, claimed to ferment at a slow rate at the entire length of large gut, contributing more fecal mass due to the bulking ability [Harris et al., 2023; McRorie Jr., 2015]. This raises the question of whether these effects of various fiber on the viscosity of the intestinal contents, the rate of passage and the formation of SCFAs has, and what, implications for the consequences of the presence of nanoparticles in the diet. The recent work of our team [Cholewińska et al., 2023] showed that dietary pectin, inulin and psyllium diminished the absorption of copper nanoparticles and protected the small intestine by strengthening the intestinal barrier via DNA repair mechanisms and inflammatory processes inhibition. Thus, it must be assumed that, in our experiment, a significant amount of copper nanoparticles had reached the large intestine of the rat together with the fiber and then appeared in the feces, modifying the enzymatic and metabolic activity of the microbiota.
It is interesting to observe whether the rapid fermentation of pectin in the rat cecum followed by its passage through the colon would leave “fiber fuel” for the fecal bacteria to produce enzymes and metabolites in the form of SCFAs. Our study results and literature data indicate that fructans, such as inulin, fructooligosaccharide or oligofructose, are well utilized by the large intestinal microbiota [Makki et al., 2018]; hence, we were intrigued before performing the analyses as to whether the enzymatic activity in the feces would be significant or meagre. In contrast, it was almost certain that psyllium residues would appear in the feces, with the reservation that this type of fiber is poorly fermented by bacteria. The results indicated that the enzymatic activity of the fecal microbiota increased after the addition of each of the three types of functional fiber. The fastest and strongest increase in enzyme activity was found as early as on the first measurement day for pectin. Interestingly, the increase in extracellular activity of the analyzed enzymes was also evident with the other fibers. Even more surprising was that, in some cases, the addition of psyllium was not inferior to the effects of pectin; this was the case, e.g., on day 1 for extracellular and total α-arabinofuranosidase, total α-glucosidase, and total β-glucuronidase activities. Such a result may indicate that the fermentation processes of psyllium already proceeding in the cecum and colon have compromised the chemical structure of this fiber or that the gel structure produced by psyllium effectively“arrested”copper nanoparticles within it. But, this was not fully confirmed by the results obtained for SCFA, as the amounts of acids produced, including acetic, butyric and propionic acids, were significantly lower than in the pectin and inulin treatments. On the other hand, the amount of SCFA produced by fecal microbiota from the psyllium groups excelled the SCFA analyzed in the CN and CNH feces. Therefore, it can be concluded that psyllium is not as inert for fermentation processes in the gut as the control fiber cellulose is. For instance, the final effect of psyllium noted on day 42 on the total activity of a marker enzyme β-glucuronidase specific to the adverse microbiota was more similar to that of inulin than pectin. High activity of β-glucuronidase is associated with pathogenic bacterial species rather than the beneficial ones [Lee et al., 2022]. The activity of β-glucuronidase is not specific only for E. coli, and it is also found in Shigella and Yersinia strains, as well as to some extent in Flavobacterium spp., Bacteroides spp., Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., and Clostridium spp. [Gao et al., 2022; Fiksdal & Tryland, 2008]. However, β-glucuronidase activity is intrinsic to more than 90% of E. coli strains, while almost all other coliform bacteria lack this activity [Poulouxi & Prodromidis, 2020]. In our previous in vivo experiments, we have shown some correlations between dietary fiber supplementation and the intensity of fermentation processes in the large intestine. In a study with rats administered a dietary grapefruit extract, inulin did not counteract clearly detrimental effects of the extract in the hindgut due to a high dose of grapefruit preparation containing not only flavonoids but also silicon dioxide and glycerol [Jurgoński et al., 2012]. This can, in some respects, be related to the effect of the high Cu-NP dose in the experiment presented here, i.e., a strong reduction in enzymatic activity and the amount of SCFAs produced despite the dietary content of functional fiber, albeit not as drastic as in the CNH group (cellulose fiber, high dose of nanoparticles). In another experiment [Juśkiewicz et al., 2007], it has been shown that the typical effect of inulin in the rat cecum is only observed when fiber level in the diet was relatively high. Furthermore, the acquired data demonstrated rapid reversibility of cecal fermentation intensity to that of the control cellulose group by removing inulin from the diet or lowering supplementation. Thus, it is reasonable to assume that, in the present experiment, the adverse effects of copper nanoparticles on the activity of the fecal microbiota would have been evident within a short time after the withdrawal of pectin, inulin and psyllium from the diet.
On day 1, the fecal ammonia content was significantly enhanced by the pectin treatment vs. cellulose and inulin treatment, regardless of Cu-NP dose (Figure 3D). A significant D×F interaction showed the highest fecal ammonia content in the PN group on all measuring days from day 2 (p<0.05 vs. all other groups). The lowest ammonia level on day 2 was determined in the CNH rat feces, while on the remaining subsequent days - in the SNH group. The t-test showed a significant increase in fecal ammonia in the PN rats on all measuring days vs. control C. The two-way ANOVA revealed that, irrespective of dietary Cu-NP dose, the inulin treatment decreased significantly fecal pH on day 1 as compared to the cellulose and psyllium treatments (Table S11 in Supplementary Materials). On the subsequent measuring days, such a decrease in fecal pH vs. cellulose treatment was noted on day 2 in pectin and inulin, on days 7 and 14 - in pectin, inulin, and psyllium, and on days 21 and 42 – in pectin and psyllium treatments. The t-test revealed that on day 2, fecal pH was decreased in the JN vs. C and in JNH vs. CH, while on day 7 – in JN, JNH, and PN groups vs. respective controls. On day 14, such a decrease was observed on fecal pH in the SN rats (p<0.05 vs. C; t-test).
A very interesting result was the content of ammonia in the feces of rats fed psyllium diets. The group of rats receiving the higher tested dose of nanoparticles along with the cellulose diet had very low levels of ammonia in the feces, and the addition of psyllium further exacerbated this decrease. It is clear that the copper nanoparticles interfered with the normal processes of digestion and absorption of proteins in the small intestine; hence, their large amount ended up in the large intestine, then in the feces, where protein fermentation is a putrefactive process. The abundance of protein available to microbial communities is one of the causes of excessive cecal ammonia generation [Griffin & Bradshaw, 2019]. But fermentation processes involve the gut microbiota, and its activity in this regard was also reduced by the addition of Cu-NP. As a result, the lower level of nanoparticles affected the observed levels of ammonia and putrefactive SCFA to a much lesser extent than the higher dose of Cu-NP. And at this point, the effect of psyllium on ammonia and putrefactive SCFA levels should be regarded as positive, since psyllium proactively reduced the levels of putrefactive substances without significantly inhibiting the enzymatic activity of the microbiota. It has been found that excessive intestinal ammonia release can damage epithelial cells by altering their morphology and disrupting their metabolism [Bell et al., 2023]. Undigested in the upper intestine amino acids, such as valine, leucine and isoleucine, may undergo the anaerobic microbial breakdown and be converted into compounds with not only strong odor but unhealthy properties as well, such as iso-butyric, iso-valeric and valeric acids, as well as cadaverine, putrescine, other amines, and hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan [Markowiak-Kopeć & Śliżewska, 2020]. Excessive accumulation of isobutyric, valeric and isovaleric acids, i.e., putrefactive SCFA, indicates malfunctioning fermentation and digestion processes [Badri et al., 2021].
CONCLUSIONS
The addition of copper nanoparticles to the diet resulted in a drastic and rapid reduction in the enzymatic activity of the microbiota in the rat feces after only the first day of feeding. This was related to both extracellular and intracellular activity. The percentage of enzyme release from the bacterial cell to the external environment in the feces was higher when nanoparticles were used in the diets, compared to control diets containing respective doses of calcium carbonate. Analyses showed that the double dose of Cu-NP had a stronger suppressive effect on bacterial enzyme activity compared to the lower dose. This was already evident after the first or second day of feeding, and this condition persisted until the end of the 42-day experiment. The addition of functional fiber to diets containing copper nanoparticles significantly increased bacterial enzyme activity compared to the diets with nanoparticles and control cellulose. The afore-mentioned effect was the strongest and most rapidly evident with pectin, while the effect of the addition of inulin or psyllium exceeded that of pectin only in some cases, i.e., α-glucosidase activity. Inulin, a typical and established prebiotic, most favorably reduced the suppressive effect of nanoparticles in relation to the fecal content of butyric acid and propionic acid in rats. However, it should be noted that this beneficial effect of inulin on the content of individual SCFAs was only apparent at the lower Cu-NP dose. In the final phase of the experimental feeding, the positive effects of the addition of inulin to the diet with nanoparticles in relation to propionic and butyric acids were also evident compared to the control group fed a diet with cellulose but lacking Cu-NP. In the case of psyllium, its addition to the diet most strongly reduced fecal ammonia formation, high concentrations of which in the intestine can be detrimental to the health status of the colonic epithelium. To summarize in one sentence, the high potential of dietary fiber in the form of pectin, inulin or psyllium in mitigating the suppressive effect of copper nanoparticles on the enzymatic and metabolic activity of the intestinal microbiota should be recognized.

