INTRODUCTION
Consumed fish represent a precious ally for human health, since fish play a keystone role as a source of animal protein, longchain n3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals [Wang et al., 2020]. Moreover, fish have a relatively low energy value thus are recommended in a healthy and balanced diet [Rubio-Rodríguez et al., 2010]. It is well known that long-chain n3 PUFAs present in fish lipids are associated with beneficial health outcomes. A high consumption of n3 PUFAs, more specifically eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n3) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n3), leads to an increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol content and a decrease in total cholesterol content, and in reduced levels of inflammatory markers [Asher et al., 2021]. Indeed, they play a key beneficial role in anti-inflammatory metabolism, being the substrates in the synthesis of biologically active anti-inflammatory mediators involved in several pathologies such as neurodegenerative disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis [Calder & Yagoob, 2009; Chitre et al., 2019; Simopoulos, 2008]. The World Health Organization (WHO) and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) recommend a regular fish consumption of at least one-two servings per week with each serving providing the equivalent of 250–500 mg of EPA+DHA [WHO/FAO, 2003].
Red mullet, Mullus barbatus (L. 1758), has a widespread geographical distribution that extends from the eastern Atlantic along the European and African coasts to the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea [Fisher, 1987]. It is one of the most valuable components of coastal Mediterranean demersal fisheries [Tserpes et al., 2002]. Although there is considerable knowledge of red mullet biology, distribution and fishery [Fiorentino et al., 2008; Tserpes et al., 2002], information on their nutritional value is very scarce. They are usually eaten cooked with different methods including boiling, frying, roasting etc. Cooking processes inevitably affect the nutritive value of fish and especially profile of flavor compounds as well as contents and quality of proteins, lipids and vitamins [Wang et al., 2020; Wei et al., 2023]. Usually high temperatures used in these processes degrade nutrients through hydrolysis and oxidation. Fatty acids, mainly PUFAs, are considered to be especially susceptible to oxidation during high-temperature culinary treatments [Bastías et al., 2017; Koubaa et al., 2012]. On the other hand, fish protein digestibility was reported to increase upon cooking, due to their denaturation. In addition, cooking was shown to improve certain features of fillets, for example by developing good odor, appealing look, and removal of harmful microorganisms [Abou-Taleb et al., 2021; Bognár, 1998; Koubaa et al., 2012].
Several studies have previously investigated the effects of different cooking methods on the nutritional quality of fish [Alexi et al., 2019; Biandolino et al., 2021; Costa et al., 2015; Gladyshev et al., 2014; Hosseini et al., 2014; Schneedorferová et al., 2015]. Koubaa et al. [2012] investigated the effect of four cooking methods on the fatty acid profile of red mullet from the sea gulf of Gabes (Mediterranean Sea). They reported the best proportion of PUFA and n6/n3 ratio in steamed, oven-cooked, and microwaved fish as compared with fried red mullet. Garcıa-Arias et al. [2003] have also reported that frying affect the fatty acid composition of sardine with decreasing EPA and DHA, while oven-baking and grilling minimally affected the fatty acid content. Therefore, it is fundamental to inform consumers about the best cooking methods that have the least adverse effect on the nutritional value of fish. This should be done on the basis of scientific studies which examine the effects of different culinary treatments on contents of essential compounds and indicators of the nutritional values of fish, such as lipid nutritional quality indices (LNQI).
The objective of the present study was to determine the effect of five in-house cooking processes (barbecue-grilling, oven cooking, frying, microwaving, and boiling) on lipid content and fatty acid profile of red mullet Mullus barbatus (L. 1758). Moreover, in order to assess the nutritional quality of the lipid fraction after cooking, a number of fatty acid-related nutritional quality indices, for the first time for red mullet, was determined. These would help select the optimal cooking method to be recommended to consumers and nutritionists for fish culinary preparation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Fish origin and preparation
Fresh specimens of Mullus barbatus (L. 1758) were purchased from a local market in the city of Taranto (Southern Italy), just immediately after being caught from the Ionian Sea (Mediterranean Sea), during spring 2021. Similarly sized fish were selected to ensure that any biochemical and chemical differences were not size-dependent (length 10.4±0.7 cm, weight 23.6±1.7 g). They were immediately stored in icebox at 4°C and transported to the laboratory for processing and analysis. Fish were washed several times in tap water, and cooked with the whole body after being gutted and scaled, without removing the head and skin. They were randomly divided into six groups: each group consisted of about 45 individuals, with 15 samples for each replicate (n=3). One group was kept fresh-raw and used as control (raw). The others were cooked with following methods: barbecuing-grilling (embers, cooking time of about 6–8 min), oven-cooking (oven, 200°C for 10–15 min), frying (pan frying with 1 L of olive oil at a temperature of about 180°C for 10 min), microwaving (Samsung M17-13 microwave oven (Suwon, South Korea), 800 W, 2,450 MHz, cooked medium-high for 5 min), boiling (on 3 L of tap water for 10 min at 90–100°C). Once cooked, fish were gently drained for about 5 min on absorbent paper towels. The fresh and cooked fish were cut into small pieces, weighed in glass containers and frozen at –20°C, to be subsequently freeze-dried and homogenized.
Moisture, total lipid content, and fatty acid profile determination
The moisture content of cooked and fresh fish was determined by drying the sample in an oven at 105°C until a constant weight was obtained according to the AOAC method [AOAC, 2005].
Lipid extraction was performed according to the modified Folch method [Folch et al., 1957]. Briefly, the fish samples were homogenized using an Ultra-Turrax homogenizer (IKA-Werke GmbH & Co., Staufen, Germany). After that, 0.5 g of homogenate of each sample was homogenized with 5 mL of a chloroform/ /methanol mixture (2:1, v/v), which contained 0.01% butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) as the antioxidant. Next, 2 mL of a 0.88% potassium chloride solution was added and mixed thoroughly. After phase separation, the chloroform was evaporated until dryness. The total lipid content was determined gravimetrically and the results were expressed as g per 100 g wet matter (wm).
The content of fatty acids (FAs) in the total lipids of M. barbatus were determined as described by Biandolino et al. [2021]. FA methyl esters (FAMEs) were analyzed on a gas chromatograph (GC) (Hewlett Packard (HP)/Agilent 6890 N, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and fitted with an Agilent HP-88 column (60 m × 0.25 mm id, 0.2 μm). Helium was used as the carrier gas (1 mL/min). The column temperature program was as follows: 150 to 250°C at 4°C/min and held at 250°C. The fatty acids were identified by comparing retention times of corresponding peaks with those of a mixture of fatty acid methyl ester standards (Supelco 37 component FAME mix, Supelco Inc. Bellefonte, PA, USA). Relative quantities were expressed as % of total fatty acids. Quantification was made also using the technique of internal standardization with methyl nonadecanoate (98% purity Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals, Saint Louis, MO, USA). The results were expressed as mg/100 g wm.
Lipid nutritional quality indices
The LNQI of both raw and cooked fish were evaluated based on the fatty acid compositions of fish lipids. Indices of PUFAs/saturated fatty acids (SFAs), (MUFAs+PUFAs)/(SFAs–C18:0), n6/n3 and n3/ /n6 ratios, EPA+DHA, arachidonic acid (ARA)/DHA and ARA/EPA ratios were evaluated. The atherogenic (AI) and thrombogenic (TI) indices were estimated according to Equations (1) and (2), respectively [Ulbricht & Southgate, 1991], whereas the ratio of hypocholesterolemic/hypercholesterolemic fatty acids (HH) was calculated according to Equation (3) [Santos-Silva et al., 2002].
where: selected PUFAs include C18:2n6, C20:4n6, C18:3n3, C20:5n3, C22:5n-3, and C22:6n3.The Equations (4) and (5) were used to calculate the health-promoting index (HPI) and the unsaturation index (UI), respectively [Chen & Liu, 2020].
where: UFAs – unsaturated fatty acids.(5)
The polyene index (PI) was estimated based on the Equation (6) proposed by Pirestani et al. [2010].
Statistical analysis
All analyses were performed in triplicate and the results were reported as mean values ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed by using Past software, version 4.03. Data were tested for normality of distributions and homogeneity of variances by means of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test and the Levene test, respectively. Mean values were compared by one-way ANOVA to test the difference in nutrients between raw and cooked samples. When significant differences were found, a post hoc Tukey test (p<0.05) was applied. When requirements for normality were not met, the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test on ranks was applied (p<0.05). Hierarchical clustering analysis was used to graphically represent differences in the nutritional quality of the raw and cooked fish studied.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Moisture and total lipids
In raw fish, the moisture content was 78.3 g/100 g of the total tissue weight and lipid content was 2.1 g/100 g wm (Figure 1). Previous studies reported slightly different data for the same species, in a range of 72–78 g/100 g for moisture content and 1.82–10.9 g/100 g wm for lipid content [Di Lena et al., 2016; Kocatepe & Turan, 2012; Prato & Biandolino, 2012; Roncarati et al., 2012]. Indeed, the chemical composition of fish varies greatly among species but also within the same species, depending on many variables, such as season and time of fishing, geographical area of fish life, feeding availability, age, sex, and physiological condition [Prato & Biandolino 2012].
Figure 1
(A) Moisture content and (B) total lipid content based on wet matter (wm) of raw and cooked Mullus barbatus. Identical letters over bars show not significant differences (p≥0.05).
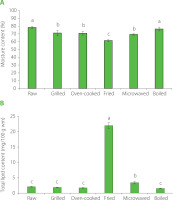
The moisture content of red mullet showed a significant (p<0.05) decrease as a result of cooking treatments (except with boiling), reaching the minimum value after frying (61.2 g/100 g) (Figure 1). The lipid content significantly (p<0.05) increased after frying, which resulted in its about ten times higher value (21.1 g/100 g wm) compared to that determined for the raw fish (2.1 g/100 g wm). A significant (p<0.05) increase was also observed for microwaved fish (3.4 g/100 g wm). These results are in accordance with the findings reported by Weber et al. [2008], Naseri et al. [2013], Gokoglu et al. [2004], and Biandolino et al. [2021], in studies on fish and molluscs bivalves, which showed a significant lipid increase after cooking, which might be mainly due to moisture loss via evaporation inducing the concentration of fat in the final product and to the absorption of frying oil by the fish [Sampels, 2015]. Moreover, Quaglia & Bucarelli [2001] stated that, during frying, the exchange between lipids and water occurred through the pores opened during the water evaporation. It has also been found that lean fish tend to absorb higher quantities of frying oils than the fatty ones [Alexi et al., 2019; Kalogeropoulos et al., 2004]. The fish samples analyzed in this study were relatively lean, which suggests high oil absorption and explains the high oil content of the fried red mullet.
Fatty acid composition
The compositions of the most important fatty acids of lipids of raw and cooked red mullet and quantities of these fatty acids expressed as % of total FAs and as mg per 100 g of wm are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. The fatty acids exceeding a minimum of 0.1% total FAs in a minimum of one sample were considered and compared among the different cooking treatments. Quantitatively, the raw fish showed a profile of fatty acids favorable to consumer health with PUFAs (552 mg/100 g wm, 38.0% total FAs) as dominant FA group followed by SFAs (530 mg/100 g wm, 36.4% total FAs), and MUFAs. The latter showing the lowest value (372 mg/100 g wm, 25.6% total FAs). Lower PUFAs content compared to SFAs and MUFAs has been reported by Kocatepe & Turan [2012] and Koubaa et al. [2012] for Mullus barbatus. In our study, the raw fish contained palmitic acid (C16:0) as the main FA, followed by oleic (C18:1n9), DHA (C22:6n3), EPA (C20:5n3), palmitoleic (C16:1n7), and stearic (C18:0) acids. It is important to highlight the high content of oleic acid (C18:1n9) (14.0% total FAs) contributing approximately to 55.6% of total MUFAs. These results were similar to those reported by Merdzhanova et al. [2012] and Koubaa et al. [2012] for the same fish species.
Table 1
Fatty acid (FA) profile (% of total FAs) of lipids extracted from raw and cooked Mullus barbatus.
[i] Values are means ± standard deviations of three separate replicates. Means with different letters (a–f) within each raw indicate significant differences (p<0.05). SFAs, saturated fatty acids; MUFAs, monounsaturated fatty acids; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; nd, not detected; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid.
Table 2
Content of fatty acids (FAs) (mg/100 g wm) of lipids extracted from raw and cooked Mullus barbatus.
[i] Values are means ± standard deviations of three separate replicates. Means with different letters (a–e) within each row indicate significant differences (p<0.05). SFAs, saturated fatty acids; MUFAs, monounsaturated fatty acids; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; nd, not detected; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acid; wm, wet matter.
Significant differences (p<0.05) were found between cooking methods, in terms of contents of total and individual saturated and unsaturated FAs (Table 1 and Table 2). It is noteworthy to consider that the variations in the fatty acid contents reflect the lipid content (Figure 1). For this reason, the fried and microwaved products showed significantly (p<0.05) higher contents of most of individual fatty acids (Table 2). When referring to the values based on the total FAs, the comparison of the raw sample with cooked ones revealed a significant (p<0.05) increase in the proportion of SFAs after most treatments, with the exception of frying (decrease from 36.4 to 18.8% total FAs, p<0.05), and oven-cooking (insignificant difference, p≥0.05). Palmitic and stearic acids were the dominant SFAs in the total FAs of cooked fish lipids, although with considerably lower values in the fried product (11.9% and 5.39% total FAs, respectively). Similar results were found by other authors for the same and other fish species [Kalogeropoulos et al., 2004; Koubaa et al., 2012; Weber et al., 2008]. SFAs are traditionally considered as unhealthy components because the favor the increase in plasma concentration of cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD), although conclusions from recent meta-analyses have not supported this association [Zhuang et al., 2019]. Certainly, among SFAs, stearic acid has a neutral effect on cholesterol concentrations and thus on CVD risk, and this may be due to desaturation that rapidly converts it to oleic acid in the liver [Micha & Mozaffarian, 2010].
Cooking methods induced variations in the proportion of MUFAs (% total FAs), with the following order boiling=grilling<microwaving<raw<oven-cooking<frying (Table 1). Fried fish lipids showed the highest MUFA contribution in total FAs (68.2% total FAs), more than 2.5 fold higher than the raw sample (25.6% total FAs). The exchange between the frying oil and the fish lipids with the MUFA absorption from frying oil resulted in modification of the fish lipid FA profile [Hosseini et al., 2014]. In our study, this resulted in a significant (p<0.05) increase of contribution of the fatty acid characteristic of olive oil (oleic acid, C18:1n9) in frying fish lipids, by about 4.7 times (66.6% total FAs), when compared to the raw sample (14.0% total FAs). A similar increase was reported by Al-Saghir et al. [2004] for fried salmon as compared to the raw one, by Kalogeropoulos et al. [2004] in a study on the effect of pan-frying in virgin olive oil on fatty acids of seafood, and by Zotos et al. [2013] for anchovies fried in olive oil. Oleic acid was the most represented MUFA in fish FAs after all cooking treatments, and in addition to frying, its contribution in the total FAs showed a significant increase after oven cooking (21.5% total FAs) (Table 1). However, a significant decrease of oleic acid contribution in the total FAs was observed in lipids of grilled and boiled fish (p<0.05). Palmitoleic acid was the second most abundant MUFA for all cooking treatments, with values ranging from 1.61 to 7.40% of the total FAs and significantly lower compared to raw sample (9.08% total FAs) (p<0.05). Literature data reported that MUFAs and especially oleic acid had positive impact on various tissues in general and a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, with decreasing LDL cholesterol concentration in serum, the myocardial infarction rate, and platelet aggregation [Karacor & Cam, 2015]. Moreover, high oleic acid consumption has contributed to the prevention of the risk of developing inflammatory diseases by increasing leukotriene A3 levels, which is an inhibitor of pro-inflammatory LTB4 [Piccinin et al., 2019].
Fish are a major source of marine-derived n3 PUFAs for the human diet. In recent years, the interest in n3 PUFAs increased because of their health beneficial effects and disease risk reduction, representing an incentive for the consumption of fish. However, fish is mainly consumed cooked; therefore, there is concern about the use of high-temperature processing, which may lead to the reduction of labile n3 PUFAs, resulting in a decrease of the nutritional value of the fish. Concerning the changes in the PUFAs before and after cooking, some important remarks can be made. In our study, a significant (p<0.05) decrease in PUFA proportion in the total FAs occurred after oven-cooking and frying treatments and a significant increase after boiling, while no significant (p≥0.05) differences were found between the other cooking methods and the control (Table 1). In particular, contribution of PUFAs in the total FAs drastically decreased in olive oil fried samples when compared to raw sample, i.e. from 38.0% to 13.0% of the total FAs. Decrease of more than half was reported in literature [Kalogeropoulos et al., 2004; Yazdan et al., 2009; Zotos et al., 2013]. However, previous studies have shown contradictory results regarding changes in the content of PUFAs of aquatic species during storage and cooking; according to some authors the PUFA contents tended to decrease [Saldanha & Bragagnolo, 2008], while other authors [Gladyshev et al., 2007] have reported that cooking methods (boiling, frying, etc.) would not have the same effect on the PUFA content in many fish species.
Among PUFAs, the contribution of beneficial n3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA, in the total FAs remained at satisfactory levels in cooked fish, although significantly (p<0.05) different than in the raw sample, except for microwaved fish, for which EPA and DHA remained unchanged (p≥0.05) compared to the control (Table 1). Both acids reached the lowest (p<0.05) proportion in the fried product, with 2.04 and 2.95% for EPA and DHA, respectively. These values were consistent with literature data [Asghari et al., 2013; Gladyshev et al., 2007; Kalogeropoulos et al., 2004; Weber et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2011; Zotos et al., 2013]. The content of EPA and DHA of fried red mullet expressed as g/100 g wm was higher than of the raw fish (Table 2). This increase can be explained by moisture loss and lipid increase during frying, but can also be due to the absorption of the fatty acids from the culinary fat used for this cooking method. Gladyshev et al. [2007] reported that among the different cooking methods (boiling, frying and roasting) used for humpback salmon processing, only frying significantly reduced EPA and DHA levels, attributing the PUFA decrease to the long duration of frying (15–20 min). In this study, the frying time was 10 min. Probably, this shorter frying time limited the oxidation and subsequent loss of PUFAs. ARA was the most abundant n6 PUFA in raw and grilled, oven-cooked, microwaved, and boiled fish followed by linoleic acid (C18:2n6) (Table 2). On the contrary, fried fish showed linoleic acid as the major n6 PUFA. The content of ARA increased significantly (p<0.05) after grilling, microwaving, and boiling compared with the raw fish.
Contribution of n3 and n6 PUFAs in the total FAs of raw red mullet lipids were 31.0% (absolute content of 451 g/100 g wm) and 6.94% (absolute content of 101 g/100 g ww) of total FAs, respectively (Table 1 and Table 2). Kocatepe & Turan [2012] found lower values than those with 11.6% for n3 and 1.49% for n6 FAs. In turn, Koubaa et al. [2012] reported 2.29 and 1.75% of the total FAs for n3 and n6, respectively. Both n3 and n6 PUFAs are fundamental for the formation of important structural lipids and elements of cell membranes. In addition, these PUFAs are precursors of eicosanoids, which influence the inflammation process and immune reactions [Simopoulos, 2008].
Cooking influenced n3 FAs proportion in the total FAs of red mullet lipids, showing a significant (p<0.05) decrease after ovencooking (24.6% total FAs corresponding to 292 mg/100 g wm), but especially after frying with a decrease from 31.0% in the raw to 7.2% in the fried fish (Table 1 and Table 2). In the case of the absolute amounts (mg/100 g mw), as already explained above, the very high content reflects the high lipid content of the fried samples. The other cooking methods did not significantly (p≥0.05) affect n3 PUFAs (Table 1). As regards the n6 PUFAs, a relative significant increase was observed with all cooking methods (p<0.05), except for frying. Despite all, the level of n3 FAs determined in raw and cooked samples was high and advantageous for human health because it prevents cardiovascular disease risk factors, while the low level of n6 FAs is required by the human body [Simopoulos, 2008].
Lipid nutritional quality indices (LNQI)
The dietary fish oil intake is associated with the prevention and treatment of different diseases, and this aspect has stimulated the need to define lipid nutritional quality indices to understand the lipids quality in fish. Among them, n3/n6 and PUFA/ SFA ratios, AI, TI, and HH are useful to assess the impact of dietary lipid intake on cardiovascular health [Chen & Liu, 2020; Ulbricht & Southgate, 1991], while the HPI, UI, and EPA+DHA are useful to evaluate the content of high-quality PUFAs [Chen & Liu, 2020]. PUFAs of n3 and n6 families differ in their antithrombogenic and anti-inflammatory activity, which is most pronounced in the n3 family, particularly EPA and DHA. Therefore, these PUFAs are useful in the prevention and treatment of several diseases, such as CVD, hypertension, type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, psychiatric disorders, obesity, and several cancers [Calder, 2006; Ulbricht & Southgate, 1991]. These findings are important and should be taken into account when making dietary recommendations.
From a health point of view, it is important to consider a balanced n3/n6 ratio (1:1), although, in recent decades, developed countries have radically modified their dietary habits, by making their diets rich in SFAs and n6 PUFAs, which has resulted in an unhealthy n3/n6 ratio. The recommended ratio differs between authors but it is always superior to 1 [Chow, 2008]. A ratio in favor of n6 PUFAs promotes the pathogenesis of many diseases, including CVD, atherosclerosis, obesity, cancer, and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases [Djuricic & Calder, 2021]. WHO/FAO [2003] recommend an n3/n6 ratio in the range of 1:8 and 1:5, as an ideal ratio, because five times higher levels of n6 FAs do not affect the conversion of n3 PUFA α-linolenic acid (18:3n3, ALA) to n3 highly unsaturated fatty acids (HUFA). The n3/n6 ratio of raw red mullet lipids was very favorable to human health, with a value of 4.47 (Table 3), and even though the n3/n6 ratio decreased for all cooking fishes (p<0.05), and in particular after frying (1.25), it was better than the above recommended standards. The significant decrease of this ratio after frying indicates that this cooking method has a high impact in the lipid quality of red mullet, suggesting a reduction of its nutritional value. Similar findings were reported by Kalogeropoulos et al. [2004] who observed an increase in the n6/n3 ratio in M. barbatus from 0.43 in raw to 1.23 in the fried sample.
Table 3
Lipid nutritional quality indices of raw and cooked Mullus barbatus.
[i] Values are means ± standard deviations of three separate replicates. Means with different letters (a–e) within each row indicate significant differences (p<0.05). SFAs, saturated fatty acids; MUFAs, monounsaturated fatty acids; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; EPAs, eicosapentaenoic acid; DHA, docosahexaenoic acids; ARA, arachidonic acid; AI, atherogenic index; TI, thrombogenicity index; HH, hypocholesterolaemic/hypercholesterolaemic fatty acid ratio; HPI, health-promoting index; UI, unsaturation index; PI, polyene index.
The PUFA/SFA ratio assumes a great importance in the evaluation of the lipid quality because dietary recommendations and policies have shown that reducing SFA intake can prevent chronic diseases [Te Morenga & Montez, 2017]. In fact, it is known that the dietary PUFAs are involved in the reduction of LDH cholesterol, and in keeping serum cholesterol at lower levels, unlike SFAs. However, just as not all PUFAs exert a positive Table 3. Lipid nutritional quality indices of raw and cooked Mullus barbatus. influence on cardiovascular prevention, not all SFAs negatively affect serum cholesterol. In general, a ratio of PUFA/SFA greater than 0.45 and at no less than 0.1 is recommended in human diets [Department of Health, 1994]. All values obtained in this study, both for raw (1.04) and cooked fish samples, were always well above the recommended value, although, a clear decrease was recorded for the fried (0.69) and oven-cooked (0.89) red mullet compared to the fresh fish (Table 3). Our results were in line with previous studies on Mediterranean species [Durmuş et al., 2019; Özogul et al., 2009]. However, the PUFA/SFA index does not take into account the important metabolic function of MUFAs in lowering LDL cholesterol levels in the blood and lowering the risk of heart disease and stroke. Similarly, it does not consider stearic acid as a SFA which does not cause the increase of plasma cholesterol [Djuricic & Calder, 2021]. For these reasons, another index was applied in which MUFAs were added and stearic acid was removed from the SFAs. The (MUFAs+PUFAs)/(SFAs–C18:0) value significantly (p<0.05) increased after frying and decreased after grilling compared to the raw samples (Table 3). For remaining cooking methods, this index did not differ significantly (p≥0.05) from the raw sample. Biandolino et al. [2021] reported a significant increase of this index with all cooking methods used in their study for mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis).
As regards the n6 PUFAs, ARA can be converted into eicosanoids, a group of lipid mediators, such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes, leukotrienes, hydroxy fatty acids, which exert essentially pro-inflammatory effects [Djuricic & Calder, 2021]. When the ARA/EPA ratio is between 1:1 and 5–10:1, both FAs are incorporated into membrane phospholipids, while when the ratio is higher, the incorporation of ARA is preferred [Whelan, 1996], determining the increases of pro-inflammatory and pro-aggregatory eicosanoids. Therefore, ARA/EPA and ARA/DHA ratios are both important, simple, rapid, and reliable indices for determining n3 FA status. In this study, all cooking methods significantly (p<0.05) increased the values of both indices of red mullet lipids, with the exception of the ARA/DHA ratio (p≥0.05) as a result of grilling (Table 3).
In order to characterize the atherogenic and thrombogenic potential of food and to overcome the weaknesses of the PUFA/ SFA ratio, considered too general, Ulbricht & Southgate [1991] developed AI and TI indices. Contrary to most indices, their lower value indicate a better food lipid nutritional quality. AI and TI less than 1.0 and 0.5, respectively, are recommended in the diet. Also for these indices, the raw and cooked red mullet showed very advantageous values. AI ranged from 0.17 (fried fish) to 0.61 (grilled fish), while TI ranged from 0.29 (raw fish) to 0.33 (oven-cooked fish) (Table 3). AI and TI of raw and cooked red mullet showed values within the ranges reported in literature for other fish, with 0.21 (Sparus aurata) to 1.41 (Kutum roach) for AI and 0.14 (Sparus aurata) to 0.87 (Oreochromis niloticus) for TI [Chen & Liu, 2020].
The ratio between hypocholesterolemic and hypercholesterolemic fatty acids (HH index) indicates the effects of specific fatty acids on cholesterol metabolism [Santos-Silva et al., 2002]. The positive effects of HH have been ascribed to HH values around 2.40 and higher values are more beneficial [Ivanova & Hadzhinikolova, 2015]. The HH indices obtained in the present study ranged from 1.90 (grilled fish) to 6.41 (fried fish) (Table 3). The HH of raw fish was 2.09. In a previous study, Prato et al. [2020] indicated a lower value (1.25) for the raw red mullet probably due to the different sampling time, physiological state, and size of fish. However, the results fall within the range found by Rincón-Cervera et al. [2020] who reported HH for fish and shellfish species from South Pacific at 2.14 for yellowtail amberjack, 2.10 for palm ruff, 1.86 for croaker, 2.00 for mackerel, 2.23 for Chilean hake, 1.73 for jack mackerel, and 1.54 for Chilean sandperch.
The major change of AI (significantly higher decrease) and HH (significantly higher increase) in our study, occurred only after frying, that was due to the absorption of oleic acid from the frying media.
The health-promoting index (HPI) is the inverse of the AI and estimates the nutritional value of dietary lipids, providing information on the effect of FA composition on CVD [Chen & Liu, 2020]. Higher the HPI is, the more the lipids are beneficial to human health [Chen & Liu, 2020]. The results obtained for raw and cooked M. barbatus showed HPI between 1.64 (grilled fish) and 5.79 (fried fish) (Table 3). The level of the latter was determined by the high content of MUFAs of lipids, not the high content of PUFAs. HPI values of red mullet were much higher than the values of 0.16–0.68 reported by Chen & Liu [2020] for dairy products; thereby confirming that eating fish is more beneficial for human health compared to dairy products.
UI is used to evaluate the content of high-quality PUFAs in lipids. In this index, a different weight is attributed to the different unsaturated fatty acids, so a high value means a high degree of total unsaturation of lipids, favorable to maintain the lipid membrane fluidity [Pekkoh et al., 2022]. In this study, UI of fried sample was the lowest (120), while these determined for boiled, grilled, and raw ones were the highest (220, 216, and 211, respectively) (p<0.05, Table 3). The UI values determined in this study for raw and cooked red mullet were generally higher than those found in other food products. Chen & Liu [2020] reported UI in ranges from 45 to 369 for macroalgae, from 125 to 155 for crops, from 73 to 124 for meat, and from 86 to 126 for dairy products.
The polyene index (PI) provides a measure of PUFA damage [Lubis & Buckle, 1990]. For red mullet, PI showed the lowest value for the fried red mullet (0.42) (Table 3), due to the lower EPA+DHA level compared to fish cooked with the other methods. All PI values, except that for the fried fish, were higher than those reported in the literature for other fish, i.e., golden grey mullet (0.32–0.55) and gold band goatfish (0.50–0.56) [Küçükgülmez et al., 2018]. In a study on the effect of cooking methods on fatty acid profile in rainbow trout, Asghari et al. [2013] reported values of PI lower than those presented in this study, but with similar trend, with fried fish showing the lowest value (0.27).
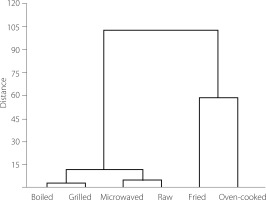
Hierarchical clustering analysis highlights graphically differences in the nutritional quality of M. barbatus, based on the fatty acid profiles (SFAs, MUFAs, PUFAs, n3 PUFAs, n6 PUFAs, EPA+DHA) and nutritional quality indices (n3/n6 ratio, PUFAs/SFAs ratio, HPI, UI, PI) (Figure 2). The fried and oven-cooked fish were clustered together because they were characterized by the lowest nutritional value, while fish cooked with the other methods formed second cluster – they were more desirable for human consumption for their beneficial lipids.
The EPA+DHA content is commonly used to assess the nutritional quality of marine animal products. The cooking of red mullet did not cause a significant (p<0.05) decrease in the relative EPA+DHA content when compared to the raw sample, except for oven-cooking and frying (Table 3). Indeed, after frying in olive oil, EPA+DHA decreased by about 5 times from 25.5% (raw fish) to 4.99% (fried fish) of the total FAs. This strong reduction was due to the olive oil uptake by fish during frying, which completely changed the fatty acid proportions. Similar results were reported by Asghari et al. [2013], Gladyshev et al. [2007], Hosseini et al. [2014], and Alexi et al. [2019]. Since the main benefits of fish consumption are mainly due to the intake of EPA and DHA, the sum of EPA+DHA represents a globally accepted index to evaluate the quality of fish. Dieticians and nutritionists are very interested in knowing the EPA and DHA content in fish to advice consumers on the optimal range of fish portion ensuring their adequate dietary intake. In this study, EPA+DHA content significantly decreased in the oven-cooked and boiled fish (p<0.05) when compared with the raw ones (371 mg/100 g mw) (Table 4). On the contrary, a significant increase of EPA+DHA was observed with frying and microwave cooking, due to highest lipid content. This fact was due to the higher total lipid triggered by these two cooking methods. Several health scientific agencies and national and international organizations have developed a series of guidelines to provide recommendations for the optimal dietary intake of EPA+DHA. The WHO/FAO [2003] and the European Food Safety Authority [EFSA Scientific Committee, 2015] recommend an intake of EPA+DHA of 250 mg for adults, with the addition of another 100–200 mg/day for women during pregnancy or lactation. According to the present study results, in order to obtain the daily intake of EPA+DHA (250–500 mg per day), it is necessary to consume a portion of only 32.5–65.1 g of fried red mullet. For the other cooking methods, a greater portion is needed to meet the daily requirement (Table 4). In a study on the effect of cooking methods on fatty acids in rainbow trout, Asghari et al. [2013] reported a portion of 154.8 g of microwaved, 234.3 g of fried, and 357.4 g of boiled trout, to ensure 1 g of EPA+DHA per day.
Table 4
Sum of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid (EPA+DHA) contents in raw and cooked red mullet (Mullus barbatus).
CONCLUSIONS
The lipid content and quality and fatty acid profile of the red mullet (Mullus barbatus) were affected by five different cooking methods examined in this study. Frying was the one that most of all affected lipid quality. Frying in olive oil markedly increased the content of oleic acid and, even if less, also of linoleic acids, while it decreased the contents of most of the other fatty acids. Based on the LNQI values, we can state that frying and oven-cooking worsened the lipid quality of red mullet, although this latter less drastically. The remaining cooking treatments, in general, caused slight changes in the fatty acid profile remaining valuable and healthier, in particular grilling and boiling appeared to be the most beneficial. Finally, for the most of cooking methods, it is sufficient to consume small portions to cover the daily intake recommended by the WHO/FAO for n3 fatty acids.