INTRODUCTION
Lipids are key components of biofilms and essential nutrients of human body. Lipid metabolism includes the processes of lipid uptake, transportation, de novo synthesis and decomposition, which produce a variety of intermediates to facilitate maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating organism functions [Kloska et al., 2020]. Aberrant lipid metabolism is involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of human diseases [Yoon et al., 2021]. Liver is the major organ responsible for the homeostatic regulation between lipid accumulation and removal. Besides lipid uptakes from food, free fatty acids transferred from blood and de novo synthesized lipids are the main sources of intrahepatic lipids. As far as the dynamic balance of liver lipids is disrupted, lipids may abnormally accumulate in liver, which eventually results in liver metabolic disorders. For instance, aberrant accumulation of triglycerides in liver may lead to liver steatosis, a hallmark feature of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [Arab et al., 2018]. NAFLD represents a kind of metabolic stress-related liver disease, which is closely associated with obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and other metabolic disorders [Lonardo et al., 2018]. Without timely intervention, NAFLD may develop into non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver cirrhosis, or even liver cancers, which severely impairs human health and lifespan.
The pathogenesis of NAFLD has not been completely elucidated, which may have hampered its effective drug treatment. Great efforts have been focused on exploring for novel medicines and interventions in lifestyle or diets to reduce NAFLD incidence and progression [Hernandez-Rodas et al., 2015]. Fortunately, a series of studies indicated that NAFLD can be effectively treated by herbal extracts with anti-hyperlipidemic and hepatoprotective activities [Abenavoli et al., 2021]. As a natural polyphenolic compound, curcumin has served as a food additive and pigment. It is also widely used as an effective herbal medicine to relieve various health problems, probably due to its multi-functional activities. In recent years, a serial of clinical and animal studies demonstrated that curcumin can mitigate hepatic lipid accumulation and exhibit anti-hepatitis effect in mice and human [Zhao et al., 2022], thereby showing good therapeutic potential for NAFLD and other metabolic disorders. Li et al. [2021] reported that 10-week food supplementation with 0.2% curcumin significantly reduced the body fat, hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance and serum lipopolysaccharide levels of obese mice. A clinical study also revealed that 102 NAFLD patients who received 8-week curcumin treatment showed significantly reduced hepatic steatosis without safety concerns [Rahmani et al., 2016]. However, due to the complex pathogenesis of NAFLD and the complicate molecular targets of curcumin, the physiological roles and action mechanism of curcumin in cellular lipid metabolism are not completely understood.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are ~22 nt small non-coding RNAs, the aberrant expression of which is closely associated with human metabolic diseases [Agbu & Carthew, 2021]. They have become potential therapeutic targets for different health problems. miRNAs may be involved in the occurrence and development of NAFLD via at least three different pathways. 1) Regulating lipid uptake through the modulation of membrane transporters. For instance, miR-26a was shown to target CD36 to inhibit lipid uptake in HepG2 cells [Ding et al., 2019]. 2) Regulating de novo lipid synthesis by targeting different enzymes. For instance, both miR-27a and miR-103 targeted and inhibited the expression of fatty acid synthase (FAS) and stearoyl-S-CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1), two key enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis, to regulate hepatic lipid metabolism and thereby alleviate NAFLD [Zhang et al., 2017; 2020]. 3) Regulating fatty acid β-oxidation in mitochondria. Veitch et al. [2022] reported that miR-30e overexpression significantly promoted exogenous fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO) in mitochondria without affecting endogenous FAO.
As one of the most abundant liver miRNAs, miR-22-3p was shown to have a physiological role in regulating lipid and metabolic homeostasis [Castaño et al., 2022; Panella et al., 2023]. Although it has been demonstrated that miR-22-3p repression improved lipid metabolism in mouse and human liver [Hu et al., 2020; Thibonnier et al., 2020], some studies showed opposite results [Gjorgjieva et al., 2020; 2022]. The exact regulatory effect and action mechanism of miR-22-3p in lipid metabolism may differ due to diverse cell types and pathological statuses investigated. Interestingly, miR-22-3p is a common polyphenol-controlled miRNA [Hayakawa et al., 2022]. Previously, we also reported that miR-22-3p was one of the molecular targets of curcumin [Sun et al., 2023]. Therefore, it is interesting to address whether curcumin regulates lipid metabolism in hepatocytes by controlling miR-22-3p and its downstream effectors.
Inducing a high-fat in vitro HepG2 cellular model by free fatty acid (FFA), this study aimed to address whether and how miR-22-3p modulated the effect of curcumin on lipid metabolism. The data revealed that curcumin effectively prevented FFA-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells, which was mitigated by miR-22-3p overexpression. Furthermore, both inhibition of miR-22-3p and overexpression of CRLS1, a target gene of miR-22-3p and key mitochondrial regulating gene, significantly reduced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Hepatic steatosis can be attributed to aberrant lipogenesis. The effects of miR-22-3p and CRLS1 on lipogenesis were also investigated. Taken together, this study is of significance to elucidate the epigenetic regulatory mechanism underlying hepatic lipid metabolism. It may also provide insights into the development and utilization of natural food supplements to relieve lipid metabolic disorders, such as NAFLD and obesity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and treatment
The human hepatoma cell line HepG2 was obtained from the Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai. HepG2 cells used in this study have a passage number not higher than 20. HepG2 cells were cultured in Gibco’s DMEM (Grand Island, NY, USA) that contained 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gemini, Calabasas, CA, USA) and a 1% penicillin/streptomycin antibiotic mixture (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA, USA). Except for specified, around 5×105 HepG2 cells per well were seeded in a 12−well plate and cultured to nearly 75% confluency. Then, a 1 mM FFA mixture (oleic acid to palmitic acid ratio of 2:1) was added for 24 h to induce lipid accumulation according to a previously described method [Gómez-Lechón et al., 2007]. To test curcumin’s activity, HepG2 cells were co-incubated with curcumin (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) and the FFA mixture for 24 h. The amount of curcumin was chosen as previously described [Shan et al., 2022]. Curcumin was dissolved in DMSO (Amresco, Solon, OH) and added to cells at 1% (v/v), and DMSO served as a vehicle control.
Cell transfection and free fatty acid induction
HepG2 cells were grown to around 75% confluency in the 12-well culture plate, followed by transfection with 40 nM miRNA (RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) or the pCMV-CRLS1 plasmid at 1.5 μg/well for 48 h using Lipofectamine 2000 Transfection Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocols. The cells were then exposed to 1 mM FFA for 24 h before further investigation. The pCMV-CRLS1 plasmid was previously prepared [Sun et al., 2023].
Oil Red O staining and lipid semi-quantification assay
The cells were in situ stained with an Oil Red O staining solution to visualize accumulation of intracellular lipid droplets, as referred to the instructions of an Oil Red O stain kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China) with modifications. Briefly, the cells were fixed with 10% formalin for 20 min at room temperature and washed twice with distilled water. Following further washing with 60% (v/v) isopropanol for 20–30 s, the cells were stained with a freshly water-diluted Oil Red O dye (0.5% stock solution and H2O in 3:2, v/v, ratio) for 20 min and then rinsed with distilled water to remove excessive dye. The stained cells were photographed under a light microscope, followed by lipid semi-quantification assay. To quantify the accumulated intracellular lipid levels, the Oil Red O-stained cells were immersed in isopropanol with 40 min vibration at room temperature to dissolve lipid droplets and the optical absorbance was measured at 510 nm [Chen et al., 2020]. The relative lipid amount was calculated as compared to that of control optical absorbance.
Determination of intracellular triglyceride and total cholesterol contents
The intracellular triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) contents were determined using the corresponding assay kits from Jiancheng Biotechnology (Nanjing, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The lipid contents were normalized to the total protein amount, and the control TG or TC level was set as 1.0.
Measurement of mRNA expression levels
The mRNA expression level was quantified using the quantitative real−time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay. Total cellular RNA was first isolated with Invitrogen’s TRIzol reagent, and 1 μg of total RNA was reversely transcribed into cDNA molecules using the Toyobo’s ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix kit (Osaka, Japan). qRT-PCR was then performed with 2 μL of properly diluted cDNA as a template per 20 μL of a reaction mix and primers at 100 nM, using the Accurate Biology’s 2× SYBR Green Premix Pro Taq HS mix (Changsha, China), under the ABI7300 real-time PCR detection system (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The PCR reactions were carried out as follows: denaturing at 95°C for 5 min, followed by 40 amplification cycles at 95°C for 5 s and 60°C for 31 s. β-actin was used as a reference gene. The relative gene expression levels were calculated by the 2−ΔΔCT method, as ΔCT = CT (tested gene) − CT (reference gene) and ΔΔCT = ΔCT (sample) − ΔCT (control). The primer sequences used in this study were as listed in Table 1 and Table S1.
Table 1
The primer sequences used in this study.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed with duplicate biological repeats for at least three times and data were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n≥3). The difference between two groups was evaluated using an unpaired Student’s t-test, and the differences among multiple groups were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and then subjected to Duncan’s analysis for multiple comparisons. Differences were considered statistically significant at p<0.05 or p<0.01.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
NAFLD represents a spectrum of liver diseases that are characterized by dysregulated hepatic lipid metabolism and is closely related to hepatocellular carcinoma [Degasperi & Colombo, 2016]. Although the prevalence of NAFLD is increasing worldwide annually, currently there is no pharmaceutical therapy available for NAFLD. However, it is generally recognized that the most effective treatment for NAFLD is patient’s lifestyle intervention, particularly physical activity and diet. In recent years, a series of studies have also indicated that plant polyphenols (such as resveratrol and curcumin) and plant extracts with polyphenols (such as tea extract), can effectively alleviate or prevent NAFLD via various pathways [Abenavoli et al., 2021]. However, the pathogenesis of NAFLD and the function mechanism of polyphenols remain largely unknown.
In general, the primary hepatocyte is the best model for in vitro NAFLD research to reveal its pathogenesis and treatment. However, due to the limited culture passages, poor reproducibility and ethical issues of primary culture, the immortalized hepatocyte-derived HepG2 cell has become a commonly used substitutive model and shows similar response to free fatty acid induction [Abenavoli et al., 2021; Gómez-Lechón et al., 2007]. Oleic acid (OA) and palmitic acid (PA) are the most abundant fatty acid components of hepatic triglycerides [Rafiei et al., 2019]. Both OA and PA were able to induce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. OA was more adipogenic but less apoptotic than PA, however, the FFA mixture (2OA/1PA) combines the advantages of both acids [Gómez-Lechón et al., 2007]. Hence, a 1 mM FFA mixture was used in this study to induce an in vitro high-fat hepatic cellular model of HepG2 cells.
Curcumin prevented lipid accumulation in free fatty acid-induced HepG2 cells
To evaluate the effect of curcumin on lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells, the cell viability was first determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in FFA and curcumin treated cells. It was shown that curcumin (up to 20 μM) did not exhibit obvious cytotoxic effect in HepG2 cells, however, a dramatic decrease in cell viability was observed upon 40 μM curcumin treatment (Figure S1A). Therefore, HepG2 cells were treated with no higher than 20 μM curcumin in the following assays. High-fat HepG2 cells were then induced by a 1 mM FFA mixture for 24 h without affecting cellular viability. And additional curcumin treatment did not significantly affect the cell viability, which remained constant after 24 h (Figure S1B). Therefore, in the subsequent assays, HepG2 cells were co-treated with 1 mM FFA and 5–20 μM curcumin for 24 h to evaluate curcumin’s effect on lipid accumulation without cytotoxic impact.
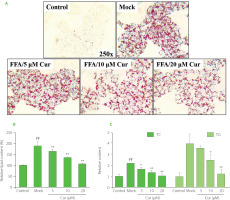
Oil Red O staining was then carried out in FFA and curcumin co-treated cells. The results showed that FFA exposure significantly induced lipid accumulation. However, curcumin co-treatment markedly decreased the amount of lipid droplets with a dose-dependent effect (Figure 1A). Further lipid semi-quantification assay results showed that FFA-induced lipid deposition was dramatically reduced by 5–20 μM curcumin by around 10–50%, which was consistent with the results of Oil Red O staining (Figure 1B). One of the characteristics of NAFLD is the dysregulation of liver lipid metabolism related to TG [Arab et al., 2018; Degasperi & Colombo, 2016]. TG and cholesterol represent the main groups of lipids in cells. TG serves as a storage form of cellular lipids, and cholesterol is the precursor of various lipid signaling molecules [Friedman et al., 2018]. Their total contents were also measured. As shown in Figure 1C, the intracellular TC and TG levels were increased by about 2.2-fold and 4-fold, respectively, upon 24 h FFA treatment in HepG2 cells. However, this stimulatory effect was attenuated by curcumin with a dose-dependent effect. Upon 20 μM curcumin treatment, the TC and TG levels were reduced to less than 50% of that of mock cells and similar to that of control cells. All these data indicated that curcumin promoted lipid metabolism, which was consistent with previous in vivo and in vitro studies [Li et al., 2021; Rahmani et al., 2016; Tian et al., 2018].
Figure 1
Curcumin prevented free fatty acid (FFA)-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Cells were co-treated with 1mM FFA mixture and various amounts of curcumin as indicated for 24 h before the assessment of cellular lipid levels. (A) Representative Oil Red O staining images. (B) Lipid semi-quantification of Oil Red O-stained cells. The control lipid content was set as 100%. (C) The total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) contents. The TC and TG levels in control cells were set as 1.0. ##p<0.01, compared with untreated control cells; *p<0.05 or **p<0.01, compared with mock cells. Cur, curcumin; Mock, FFA-induced control cells.
Curcumin inhibited lipid accumulation by downregulating miR-22-3p expression
miRNAs have been reported to be involved in the pathogenesis of fatty liver diseases with therapy potentials [Agbu & Carthew, 2021]. They may regulate lipid metabolism through downstream pathways and function as potential drug targets for NAFLD. For example, miR-122 inhibition upregulated its target gene SIRT1, a lipogenesis inhibitor that can activate the AMPK pathway to eventually prevent FFA-induced lipogenesis [Long et al., 2019]. And miR-32-5p may activate SREBP-mediated adipogenesis, eventually promoting liver lipid accumulation and metabolic disorders [Wang et al., 2023]. In addition, miR-122, miR-33, miR-34a and miR-21 are potential biomarkers for NAFLD and closely related to its progression [Gjorgjieva et al., 2019]. Interestingly, curcumin can exert its physiological activity via miRNA regulation [Hayakawa et al., 2022]. Our recent study also showed that miR-22-3p was downregulated by curcumin and modulated its antioxidant activity [Sun et al., 2023]. miR-22-3p is known to be involved in cytokine production, tumor and metabolic diseases, and is also involved in regulation of lipid metabolism [Panella et al., 2023], however, with controversial effects [Castaño et al., 2022; Gjorgjieva et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2020].
To address whether and how miR-22-3p also modulates curcumin’s activity in controlling lipid metabolism, the expression level of miR-22-3p and its function in HepG2 cells were further examined. Compared with the control, FFA induction significantly increased miR-22-3p expression level. And additional curcumin treatment significantly declined the miR-22-3p level to around 60% (Figure S2A). Thus, the miR-22-3p expression level varied along with altered lipid amount in HepG2 cells. It was elevated by FFA but downregulated by curcumin. Moreover, miR-22-3p attenuated curcumin’s effect in preventing lipid accumulation. The results showed that curcumin-caused lipid reduction in HepG2 cells was reversed by miR-22-3p, as red lipid droplets and the total lipid contents were significantly increased by 48 h pre-transfection of miR-22-3p in the curcumin-treated cells (Figure 2A−B). All these data indicated that miR-22-3p is involved in modulating curcumin’s activity in lipid control.
Figure 2
miR-22-3p modulated curcumin’s effect on preventing free fatty acid (FFA)-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. (A–B) miR-22-3p overexpression reversed curcumin’s effect on preventing lipid accumulation. Cells that were transfected with 40 nM miR-22-3p mimic for 48 h, and then co-treated with 1 mM FFA and 20 μM curcumin (Cur) for 24 h. (A) Representative Oil Red O staining images. (B) Lipid semi-quantification of Oil Red O-stained cells. Different low case numbers on top of the columns indicate statistically significant differences among samples. (C–E) miR-22-3p repression significantly prevented lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. The cells were transfected with 40 nM miR-22-3p inhibitor (anti-miR-22-3p) for 48 h and then stimulated with 1 mM FFA for 24 h. (C) Representative Oil Red O staining images. (D) Lipid semi-quantification of Oil Red O-stained cells. (E) The total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) contents. The TC and TG contents in control cells were set as 1.0. *p<0.05 or **p<0.01, compared with control cells that were transfected with miRNA inhibitor control (anti-NC).
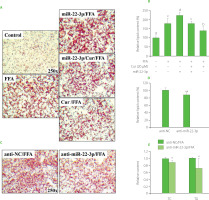
To further verify the effect of miR-22-3p on FFA-induced lipid accumulation, HepG2 cells were transfected with miR-22-3p inhibitor for 48 h and then stimulated by FFA for 24 h before lipid assessment. Compared with the control, deposition of red lipid droplets and the total lipid contents were significantly reduced upon miR-22-3p inhibition (Figure 2C−D). In addition, miR-22-3p repression significantly reduced the TC and TG contents to around 80% and 60%, respectively, as compared to the control cells (Figure 2E). Thus, miR-22-3p may function to promote hepatic lipid accumulation. Taken together, these results indicated that curcumin reduced FFA-induced lipid accumulation by downregulating miR-22-3p. miR-22-3p is a molecular target of curcumin to control lipid metabolism. Interestingly, miR-22-3p is a downstream effector of nuclear receptor farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which is regulated by curcumin in liver [Yan et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2021]. Therefore, downregulation of miR-22-3p by curcumin may be mediated by FXR.
The CRLS1 gene overexpression decreased lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells
miRNAs are involved in the regulation of cellular physiology and lipid metabolism via modulation of their target genes. For instance, miR-34a regulated macrophage cholesterol efflux and transport via targeting the ABCA1 and ABCG1 genes [Xu et al., 2020]. And miR-17-5p upregulated adipogenic differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells via repressing Tcf7l2, a Wnt signaling pathway effector [Tian et al., 2018]. Our previous study showed that the CRLS1 gene is a target gene of miR-22-3p [Sun et al., 2023]. CRLS1 encodes cardiolipin synthase 1, which catalyzed the final step of mitochondrial cardiolipin synthesis. Cardiolipin is highly expressed in liver and plays an important role in hepatocyte lipid metabolism [Tu et al., 2020]. The current study showed that the CRLS1 gene expression was significantly decreased in FFA-induced HepG2 cells, but significantly increased by around 40% upon additional 20 μM curcumin treatment (Figure S2A). In consistent, transfection with miR-22-3p inhibitor significantly promoted CRLS1 gene expression in the FFA-induced mock cells (Figure S2B).
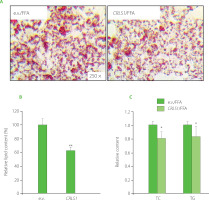
Considering the regulatory effect of miR-22-3p on lipid accumulation, CRLS1 may be also involved in lipid metabolic control. Therefore, a pCMV-CRLS1 overexpression plasmid [Sun et al., 2023] was transfected into HepG2 cells for 48 h, followed by FFA-stimulation. There was a significant decrease in lipid droplets and cellular lipid content upon pCMV-CRLS1 transfection (Figure 3A–B), which was consistent with miR-22-3p inhibition or curcumin treatment. Meanwhile, CRLS1 overexpression decreased the intracellular TC and TG levels by around 20% and 15%, respectively (Figure 3C). These data indicated that CRLS1 overexpression prevented lipid accumulation in FFAinduced HepG2 cells, which resembled the effect of miR-22-3p repression or curcumin treatment. Our study result was consistent with the findings reported by Kawata et al. [2017] who demonstrated that an MCH1 receptor antagonist showed anti-obesity and anti-hepatosteatosis effect along with elevated cardiolipin level in liver. And miR-22-3p may promote lipid accumulation via inhibiting CRLS1 expression and activity, which further affects mitochondrial lipid metabolism and mitochondrial functions.
Figure 3
CRLS1 overexpression prevented free fatty acid (FFA)-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. The cells were transfected with the pCMV-CRLS1 vector (CRLS1) for 48 h and then treated with 1 mM FFA for 24 h. (A) Representative Oil Red O staining cell images. (B) Lipid semi-quantification of Oil Red O-stained cells. (C) Quantification of the total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) contents. The TC and TG contents of control cells were set as 1.0. *p<0.05 or **p<0.01, compared with control cells that were transfected with an empty vector (e.v.).
Both miR-22-3p and CRLS1 modulated the expression of lipogenic genes
The imbalance between synthesis and decomposition of fatty acids may lead to the accumulation of lipids. Lipid synthesis is regulated by a variety of enzymes and transcription factors via different metabolic pathways. FAS encodes fatty acid synthase, the key enzyme for de novo fatty acid synthesis [Yoon et al., 2021]. The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) promotes steatosis [Lee et al., 2012]. The sterol-regulatory element binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) is involved in cholesterol metabolism and regulates TC synthesis, and liver X receptor (LXR) was shown to activate SREBP-1c and upregulate the expression of FAS [Calkin & Tontonoz, 2012; Zhao et al., 2022]. To elucidate the possible molecular mechanism underlying modulation of lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells, the expression of genes associated with lipogenesis was further examined. As shown in Figure 4A, the lipogenic genes, including SREBP-1, PPARγ, FAS and LXRα, were all dramatically upregulated by FFA, indicating lipid generation. However, additional curcumin treatment for 24 h significantly suppressed expression of these genes. Therefore, curcumin downregulated lipogenic gene expression, which was in line with its activity in preventing lipid accumulation or steatosis [Rahmani et al., 2016].
Figure 4
Both miR-22-3p repression and CRLS1 overexpression resembled curcumin’s effect on preventing the expression of lipogenic genes. (A) Effect of curcumin on the expression of genes involved in lipogenesis. The cells were co-treated with 20 μM of curcumin and 1 mM free fatty acid (FFA) for 24 h before subsequent quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) assay. (B–C) The expression of lipogenic genes was significantly decreased by miR-22-3p repression or CRLS1 overexpression. The cells were transfected with miR-22-3p inhibitor (anti-miR-22-3p) or the CRLS1 overexpression vector (CRLS1) for 48 h and then stimulated with 1 mM FFA for 24 h, followed by qRT-PCR assay. (B) Transfection with miR-22-3p inhibitor. (C) Transfection with the pCMV-CRLS1 vector. The mRNA expression level was set as 1.0 in control cells. ##p<0.01, compared with control cells; **p<0.01, compared with FFA-induced mock cells. Cur, curcumin; anti-NC, miRNA inhibitor control; e.v., empty vector.
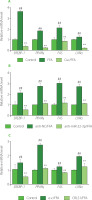
Furthermore, the mRNA levels of SREBP-1, PPARγ, FAS and LXRα genes were dramatically reduced in cells transfected with miR-22-3p inhibitor for 48 h, which was similar to curcumin regulation (Figure 4A–B). Similarly, expression of these genes was significantly reduced upon CRLS1 overexpression in FFA-stimulated HepG2 cells for 48 h (Figure 4C). Therefore, both miR-22-3p repression and CRLS1 overexpression reduced lipogenesis, which resembled the regulation by curcumin. Besides CRLS1, miR-22-3p may target multiple mRNAs and regulate different enzymes or signal molecules in lipid metabolism. For instance, miR-22-3p was shown to target PPARα and SIRT1 [Azar et al., 2020]. The current study showed that lipogenic PPARγ, SREBP-1, FAS and LXRα genes were also regulated by miR-22-3p and CRLS1. PPARγ is a ligand-activated transcription factor that controls fatty acid metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. Activated PPARγ promotes the expression of proteins involved in lipid uptake, TG storage and lipid droplet formation [Lee et al., 2012]. In addition, the PPARγ-LXRα-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway is associated with cholesterol efflux [Zhang et al., 2023]. SREBPs regulate cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis, and SREBP-1 mainly activates genes required for fatty acid and TG synthesis. And FAS is a downstream gene of SREBP-1 in lipid metabolism [Zhao et al., 2022]. Therefore, curcumin may reduce lipogenesis by downregulating the miR-22-3p/CRLS1 pathway, and eventually preventing steatosis. Curcumin may also regulate other lipid metabolic branches, as indicated by controlling the expression of genes involved in fatty acid β-oxidation and cholesterol metabolism (Figure S3). However, the exact transcriptional mechanism remains to be elucidated, and the control of gene expression/ activity by miR-22-3p/CRLS1 is still in progress.
It has been suggested that simple steatosis can lead to the progression of NAFLD along with oxidative stress or mitochondrial dysfunction [Buzzetti et al., 2016]. To address whether and how miR-22-3p/CRLS1 controls oxidative stress in high-fat hepG2 cells, the cellular ROS levels were measured. The results showed that FFA-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells was significantly decreased upon inhibiting miR-22-3p or promoting CRLS1 expression, resembling the antioxidant effect of curcumin (Figure S4). CRLS1 was previously shown to control oxidative stress in hepatic LO2 cells [Sun et al., 2023]. Tu et al. [2020] also reported downregulated CRLS1 expression in a mouse NASH model, which further promoted NASH through downstream activating transcription factor3 (ATF3). The mitochondria play important roles in controlling hepatic cellular redox balance and lipid metabolism. However, long-term stress, such as oxidative stress and lipid accumulation, may lead to mitochondrial dysfunction [Wang et al., 2022]. CRLS1 catalyzes the biosynthesis of cardiolipin, a key mitochondrial regulator and also precursor of lipid signal molecules. Peng et al. [2018] demonstrated that the progression of NAFLD may be attributed to mitochondrial dysfunction and that cardiolipin level increased in early NAFLD but decreased in NASH, which suggested cardiolipin-mediated mitochondrial control in early NAFLD. Therefore, the current study also provides a mechanistic link between NAFLD and mitochondria regulation.
CONCLUSIONS
The regulation of lipid metabolism by miRNAs is very complicated. There are a variety of miRNA species involved, which is also linked to the target mRNA network. Besides binding to the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of target mRNAs in most cases, miRNA may bind to 5′-UTR or coding sequence (CDS) of target mRNAs to control their expression. In addition, a single miRNA may have multiple targets to function in different pathways, or even exhibiting opposite effects in different hepatic steatosis models. The target gene may also be controlled by different miRNAs and show different regulatory functions. Moreover, in vivo and in vitro research data may differ, and data may even differ in different tissues of the same body. Finally, the expression and activity of miRNAs and target mRNAs do not always link with each other. Therefore, addressing the epigenetic regulation by miRNAs in lipid metabolism is of significance to reveal the pathogenesis of related liver diseases. It may also provide novel insights into the pre-diagnosis and treatment of hepatic lipid disorders.

