INTRODUCTION
With the global population surpassing 8 billion, the search for new alternative food sources has become imperative. This population growth is linked to improved quality of life, better access to healthcare, advancements in medicine, and enhanced hygiene. Consequently, scientists are compelled to find new food sources to meet the energy requirements of a growing population [Mariutti et al., 2021]. One such source can be edible insects, which are a staple food in many Asian countries, have been a kind of a traditional dish for many generations, and are considered a delicacy. In recent years, entomophagy (the consumption of insects) has garnered increasing interest in European countries, both from scientific perspectives (studying their nutritional composition, health effects, and consumer acceptance) and in terms of actual consumption [Menozzi et al., 2017].
It is estimated that nearly 2,000 insect species are considered edible worldwide. Specifically, Ramos-Elorduy [2009] identifies 2,086 edible species, Mistuhashi [2016] reports 2,141 species, and van Itterbeeck & Pelozuelo [2022] list 2,111 species. Insects can be consumed in various forms, including whole insects subjected to heat treatments (e.g., boiling, roasting, frying, drying) or in powdered form (e.g., as an ingredient in bread or pasta). However, a significant barrier to their adoption in Europe is the psychological aspect. European culture traditionally views insects as pests rather than as a viable food source. Consequently, the European population is mostly not ready to incorporate edible insects into their daily diet, with additional concerns regarding health safety and hygiene further impeding their acceptance.
Interest in edible insects is primarily a result of their high content (30−77 g/100 g) of complete, highly digestible (76.6−98%) protein [Kim et al., 2019]. Besides being a rich protein source, edible insects provide several other essential nutrients. The second largest component of edible insects is fat, which shows significant potential for use in the food industry. However, its application requires a detailed understanding of the chemical composition, as the nutritional value, technological, and functional properties of food products depend on it [Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2021]. The fat content in dry matter of edible insects varies by species. When analyzing 236 edible insects, Rumpold & Schlüter [2013] found that the average fat contents per order ranged from 13.41 g/100 g for Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets, and locusts), which are rich in protein, to 33.40 g/100 g for Coleoptera (beetles and bugs). Aguilera et al. [2021] reported even higher fat contents of 50.1 g/100 g in freeze-dried ant larvae and 40.6 g/100 g in mealworm larvae. The fat fraction in edible insects is composed mainly of triacylglycerols (approximately 80%), with smaller amounts of phospholipids (up to 20%), cholesterol, free fatty acids (FFA), and wax esters [da Silva Lucas et al., 2020]. Notably, insect-derived fat has a high nutritional value due to the presence of unsaturated essential fatty acids such as linoleic and α-linolenic acids [Udomsil et al., 2019]. The favorable fat profile of edible insects can significantly increase the polyunsaturated fatty acid content in enriched food products [Acosta-Estrada et al., 2021]. In addition to enhancing nutritional value, the incorporation of insect powder can influence the physical and sensory properties of food products [Kim et al., 2022]. Fats in baked products contribute to tenderness, flavor release, mouthfeel, and the reduction of gluten structure, as well as imparts functional properties. Due to their high-quality fat content, edible insects can replace some of the fat used in baking, thereby increasing the nutritional value of the final product [Delicato et al., 2020].
Given the high nutritional value of edible insects, a growing number of researchers has investigated the feasibility of incorporating insect powder to food products such as baked goods, bars, cakes, and cookies [Delicato et al., 2020; Kowalski et al., 2022a,b; Sriprablom et al., 2022]. Current research primarily focuses on using insects to increase the protein content of these products.
To the best of our knowledge, the lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus) is still scarcely utilized in food production, despite being a superior protein source comparable to the house cricket (Acheta domesticus), which is the most popular insect farmed exclusively for human consumption [Kurečka et al., 2021]. It is noteworthy that the European Commission has recently authorized the placing on the market of frozen, paste, dried, and powdered forms of lesser mealworm larvae (on 5 January 2023) [van Huis, 2023]. The literature indicates that this insect is characterized by a short life cycle and feeds on a varied organic matter, including agricultural and food by-products and wastes, making it relatively easy to farm and also that it contains bioactive compounds with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties that may elicit benefits to human health [Siddiqui et al., 2024]. To date, Roncolini et al. [2020] used lesser mealworm powder (10% to 30% wheat flour replacement, w/w) to produce wheat snacks. Ortolá et al. [2022] compared biscuits formulated with lesser mealworm and yellow mealworm flours, while Mazurek et al. [2023] and Skotnicka et al. [2022] compared the same types of flours as ingredients in wheat pancakes. In turn, Kowalski et al. [2022b; 2023] studied nut bars and sponge cakes with the addition of powders of three insects (yellow mealworm, house cricket, and lesser mealworm). Although these cited studies indicate an increase in the nutritional value of the final product, their findings are often inconclusive, highlighting the need for further research, particularly regarding product stability.
Therefore, this study aimed to compare the physical, sensory, and nutritional characteristics of shortbread cookies without and with the incorporation of insect powders from two edible insects: lesser mealworm larvae and house cricket imago. Additionally, the quality of the insect powder, including fatty acid composition, degrees of fat hydrolysis and oxidation, and sorption properties, was evaluated to help understand its impact on the stability of the enriched products.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials and reagents
The primary raw materials were powders derived from the larvae of lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus) (Isaac Nutrition, Cologne, Germany) and the adult form (imago) of house cricket (Acheta domesticus) (SENS Food, London, United Kingdom), which were purchased from online stores. The other ingredients required to prepare the shortbread cookies, such as wheat flour type 550, butter (minimum milk fat content 82%), white sugar, and salt, were sourced from local stores in Olsztyn, Poland. These ingredients were characterized by their appropriate shelf-life and typical organoleptic characteristics.
All reagents used in the study, including acetic acid, chloroform, methanol, n-hexane, potassium hydroxide, sodium thiosulfate, sulfuric acid, potassium iodide, and zinc, were of the analytical grade and were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA).
Measurements of color parameters of the insect powders
The color of the insect powders was measured using digital image analysis, which employed a Nikon DXM 1200 digital camera (Amsterdam, Netherlands) with a resolution of 1,280×1,024 pixels (1.4 million pixels), KAISER RB HF lighting (Buchen, Germany) consisting of four lamps with a color temperature of 5,400 K, and a computer with an image capture card and LUCIA G software v. 4.80 (Prague, Czech Republic). The study used the CIE L*, a*, b* color space, where L* denotes brightness (values in the range of 0–100%, from black to white color), a* denotes green (negative values) or red (positive values) color intensity (values from −120 to +120), and b* denotes blue (negative values) or yellow (positive values) color intensity (values from −120 to +120). Samples of each powder were placed in a Petri dish under the camera lens, and 10 images were captured and subsequently analyzed using the LUCIA G software.
Analysis of the proximate composition of the insect powders
The contents of the following compounds were analyzed in the insect powders using the official methods of AOAC International [AOAC, 2000]: water content (method no. 930.15), protein content (method no. 990.03), fat content (method no. 920.39), ash content (method no. 942.05), and fiber content (method no. 962.09). The carbohydrate content was determined by difference, i.e., the residual weight after subtracting amounts of water, protein, fat, ash, and fiber. The results were expressed in g per 100 g of insect powder.
Analysis of the sorption properties of the insect powders
Water activity (aw) of the insect powders was measured using an AquaLab 4TE instrument (AS4 v. 2.14.0 2017 from Decagon Devices, Inc., Pullman, WA, USA) with an accuracy of ± 0.0003 at 20°C [Ruszkowska et al., 2022].
The assessment of sorption properties was carried out using the static method by determining sorption isotherms and the humidity equilibrium between the sample and the atmosphere with a controlled relative humidity, adjusted using saturated salt solutions. The samples were placed in a hygrostat with aw ranging from 0.07 to 0.98 and stored for 30 days at 20°C±1°C. The mathematical descriptions of the sorption isotherms were derived using the Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) model within the aw range of 0.07 to 0.33. Parameters such as monomolecular layer capacity (vm), energy constant (ce), and specific sorption area (SSA) were determined [Tańska et al., 2017]. The results were analyzed using Jandel-Table Curve 2D software v. 5.01 (Systat Software Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). The fit of the empirical data to the BET equation was characterized by the determination coefficient (R2), the sum of squared deviations of the theoretical from empirical values (SKO), the values of standard errors (RMS) and the standard error of fit (FitStdErr).
Analysis of the fat quality of the insect powders
The fat quality in the insect powders was evaluated by determining the degree of hydrolysis (acid value) and oxidation (peroxide value), as well as the fatty acid composition. Firstly, fat was extracted from the powder using n-hexane in a Soxhlet apparatus [Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2014].
The acid and peroxide values of the extracted fat were determined according to AOCS Official Methods [AOCS, 2009] (methods Te 1a–64 and Cd 8b–90, respectively). Each powder was analyzed in triplicate.
The fatty acid composition of the extracted fat was determined following the procedure described by Mikołajczak et al. [2022]. Fatty acid methyl esters (FAME) were prepared by methylation at 70°C for 2 h with a mixture of methanol, chloroform and sulfuric acid in ratio of 100:100:1 (v/v/v). Zinc powder was then used to neutralize the sulfuric acid, and the solvents were evaporated under a stream of nitrogen. The obtained FAME was dissolved in n-hexane, centrifuged (5417R type centrifuge, Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany) for 10 min at 25,000×g, and analyzed by gas chromatography mass spectrophotometry (GC-MS) using a QP2010 PLUS device (Shimadzu, Tokyo, Japan). A capillary column (BPX-70, 25 m × 0.22 mm × 0.25 μm, SGE Analytical Science, Ringwood, Australia) and helium at a flow rate of 1.3 mL/min were used for the FAME separation. The interface and ion source temperatures were set at 240°C, while column temperature was programmed in the range of 150–250°C. The electron energy of 70 eV was applied. Fatty acids were identified based on their mass spectra, and their contents were expressed as a percentage of total fatty acids based on peak areas. Each powder was analyzed in triplicate.
Preparation of shortbread cookies
The recipe of control cookies comprised 498.34 g of wheat flour, 332.23 g of butter, 166.11 g of sugar, and 3.32 g of salt. In other cookie variants, 10% or 20% (w/w) of wheat flour was replaced by the insect powder, with no changes to the other ingredients. Cold butter, previously cut into smaller pieces, was added to the bowl of the mixer along with the powdered sugar specified in the recipe. The ingredients were mixed for 5 min in a mixer (GM-2, Bydgoszcz, Poland). Subsequently, the pre-sifted wheat flour, or its mixture with the designated proportion of the insect powder, and salt, were added to the bowl and mixed again for 5 min. The kneaded dough was set aside to cool at 5°C for 30 min. After cooling, the dough was rolled out with a rolling pin into ribbons 5 mm thick. Star-shaped cutters with a diameter of 50 mm were used to shape the dough. Each batch of dough yielded 48–50 cookies. The cookies were baked in a convection-steam oven type XVC105 (UNOX, Sp.A., Cadoneghe, Italy) at 180°C for 10 min. After baking, the cookies were allowed to cool for 2 h at 21°C before testing. Two independent production runs were conducted for the analyses.
Analysis of the color parameters of the cookies
The color of the shortbread cookies was measured using digital image analysis, following the method described above for the color analysis of the insect powders with some modifications. The cookies were prepared by slicing 1 cm from the center of the cookie, and images (10 for each sample) of the crosssection were analyzed. Additionally, the total color differences (ΔE) were calculated using the formula (1):
where: ΔL*, Δa*, and Δb* represent the differences in the L*, a* and b* parameters between the control cookies and the fortified cookies, respectively.Analysis of the fat quality and oxidative stability of the cookies
The analyses of fat quality (degree of hydrolysis and oxidation, and fatty acid composition) in the shortbread cookies were performed as described above for the insect powders. Additionally, the oxidative stability of the cookies was evaluated using a 743 Rancimat (Metrom, Zofingen, Switzerland) eight-channel oxidative stability instrument. Cookie samples (2.5 g each) were placed in a reaction vessel within a thermostatic electric heating block. The temperature was set to 110°C, and the airflow rate was 20 L/h. Oxidative stability was expressed as induction time in hours. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate.
Analysis of the nutritional value of the cookies
The analyses of the nutritional value (content of protein, fat, ash, fiber, and water) of the shortbread cookies were performed as described above for the insect powders. Additionally, the total energy was calculated using conversion factors of 4 kcal/g for carbohydrates, 4 kcal/g for proteins, and 9 kcal/g for fat.
Analysis of the consumer acceptance of the cookies
A group of 41 randomly selected individuals, including 27 women and 14 men, from the Faculty of Food Science at the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland, participated in the consumer acceptance test of the cookies. The evaluation took place 24 h after baking at room temperature. Characteristics of the cookies were assessed using a structured linear scale, where 0 points represented the lowest rating and 10 points represented the highest rating. The following characteristics of the cookies were addressed in the evaluation: taste (0 – foreign, undetectable taste, 10 – peculiar, buttery), aroma (0 – extraneous odor, undetectable, 10 – sweet, buttery odor), brightness of the surface color (0 – dark color, 10 – light color), uniformity of the surface color (0 – non-uniform color, 10 – uniform color), consistency (0 – soft, non-crunchy, 10 – hard, crunchy), and texture (0 – very little force needed to break, 10 – very much force needed to break). All cookie samples were coded to prevent evaluators from identifying the type of cookie [Mieszkowska & Marzec, 2015].
Statistical analysis
All results were presented as mean values ± standard deviations. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by the Tukey test, was performed to analyze significant differences between the samples (p≤0.05). The analysis was performed using Statistica v. 13.3 software (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Color parameters and proximate composition of the insect powders
The color of products is a crucial determinant of consumer choice [Alhujaili et al., 2023]. In the case of unconventional ingredients, such as insect powders, color can contribute to either positive perception of a product or to its rejection, being an important element of food neophobia. The results of the insect powder color measurements are shown in Table 1. Statistical analysis revealed significant differences (p≤0.05) among the insect powders in all evaluated color parameters. The L* value was approximately 25% higher in the lesser mealworm powder (LMP) compared to the house cricket powder (HCP). The positive values of a* and b* were measured, pointing to the presence of red and yellow colors, respectively. The color of LMP was less red (lower a* value) and more yellow (higher b* value) than the color of HCP. In contrast, house cricket powder studied by Singh [2020] showed lower L* (47.8−52.3) and b* (8.38−11.2) values and higher a* values (3.73−4.28). Unfortunately, there is a lack of research on the color parameters of lesser mealworm powder to enable any conclusive comparisons.
Table 1
Physical and chemical characteristics of lesser mealworm powder (LMP) and house cricket powder (HCP).
When analyzing the differences between the proximate composition of the powders from the two types of insects, statistically significant differences (p≤0.05) were noted for all compounds (Table 1). Specifically, LMP had a higher water content compared to HCP, which was likely attributed to differences in the chemical composition of the raw materials, the degree of processing, and the technological parameters of the drying process employed by the manufacturers. For comparison, Udomsil et al. [2019] reported a water content of 6.3% in the powder from dried adult house crickets and 3% in the powder from field crickets. In contrast, Osimani et al. [2018] showed a higher water content (9.40%) in HCP.
LMP had a nearly 40% higher fat content compared to HCP (Table 1). Conversely, HCP contained higher levels of protein, carbohydrates, fiber, and ash compared to LMP. Alike differences in the content of chemical compounds in powders from these insects were observed by Kowalski et al. [2022a, 2023]. Interestingly, the contents of compounds determined in this study differ from those reported by the cited authors, despite using insect powders produced by the same manufacturers. This discrepancy highlights the significant heterogeneity of insect powders, likely influenced by the insects’ origin, processing conditions, and storage duration. Therefore, the future mass production of products containing edible insects may pose a challenge due to the unpredictable quality of these raw materials. Ensuring consistent quality is critical for the widespread acceptance and success of edible insect products.
Sorption properties of the insect powders
Water content and water activity are fundamental parameters that influence the chemical, physical, and microbiological product quality [Mathlouthi, 2001]. These parameters characterize a product’s ability to adsorb and desorb water from the environment depending on the potential difference between the product and its environment [Mathlouthi, 2001] and they are critical for the storage stability of products. The water activity (aw) of the insect powders is shown in Table 2. The aw of LMP was found to be 0.383, which is 1.5 times higher than the aw of HCP. The determined aw values indicated that the insect powders had ensured microbiological stability, since a minimum aw for yeasts and molds proliferation is 0.61, with filamentous fungi being the predominant microorganisms in food products [Tapia et al., 2020]. Marzoli et al. [2023] found similar values of aw for house cricket powders stored at room temperature for one year.
Table 2
Water activity (aw) and parameters of Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) model used to describe the sorption isotherms of lesser mealworm powder (LMP) and house cricket powder (HCP).
| Characteristic | LMP | HCP |
|---|---|---|
| aw | 0.383±0.003a | 0.254±0.002b |
| vm | 3.5929 | 3.2517 |
| ce | 27.86 | 24.38 |
| R2 | 0.9719 | 0.9988 |
| SKO | 0.8485 | 0.1691 |
| RSM (%) | 1.4846 | 0.5298 |
| FitStdErr | 0.1029 | 0.0509 |
| SSA (m2/g) | 126.23 | 114.25 |
[i] Results of aw are shown as mean ± standard deviation (n=3). Different letters within the row with aw indicate significant differences between the powders (p≤0.05). vm, monolayer capacity; ce, energy constant; R2, determination coefficient; SKO, sum of squared deviations of the theoretical from empirical values; RMS, standard error; FitStdErr, standard error of fit.; SSA, specific sorption area.
The sorption isotherms of the insect powders are shown in Figure 1A. Evaluating the course of the isotherms, it was found that they were characterized by a sigmoidal shape, showing similarity to type II isotherms according to the classification proposed by Brunauer [Mathlouthi, 2001]. Both isotherms demonstrated a continuous course over the entire range of aw (0.07−0.98) (Figure 1A), suggesting no significant change in the structure determined by an increase in the degree of ordering of the individual components in the products. LMP sorption isotherm showed that the water desorption process occurred in the I area (aw in the range of 0.07−0.33). In the case of HCP, the desorption process was in the narrower aw range of 0.07−0.11. Analysis of the graphical course of sorption isotherms also showed that for areas II and III, a higher equilibrium water content was determined for LMP. In the environment with aw of 0.75 (isotherm area II), the equilibrium water content for LMP was 15.38 g/100 g d.m., and in the environment with aw of 0.98 (isotherm area III) it was 38.30 g/100 g d.m.
Figure 1
The sorption isotherm (A) and water activity, aw (B) of lesser mealworm powder (LMP) and house cricket powder (HCP) after storage for 30 days at 20°C in an environment with aw in the range of 0.07–0.98 (n=3). I, first isotherm area (aw=0.07−0.33); II, second isotherm area (aw=0.33−0.75); III, third isotherm area (aw=0.75−0.98); d.m., dry matter.
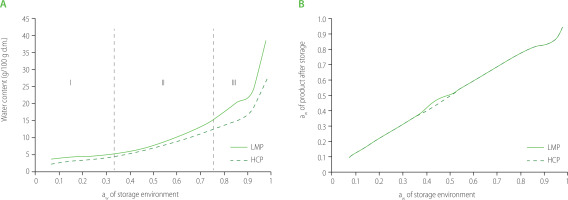
Based on the sorption isotherms, it can be hypothesized that the differences in the hygroscopicity of the tested products were mainly determined by their chemical composition. The HCP had a slightly higher protein content compared to the LMP, as well as a higher fiber content and a lower fat content (Table 1). These differences explain the higher equilibrium water content observed in the areas II and III of the sorption isotherm. Similar shapes of water sorption isotherms for bread flour (wheat) were found by Moreira et al. [2010] and for tapioca flour by Chisté et al. [2012].
The water activity of the insect powders after storage for 30 days in a hygrostat with constant relative humidity in the range of environmental aw of 0.07−0.98 showed that the powders did not reach the level of environmental water activity (Figure 1B). However, the LMP reached higher water activity after 30 days of storage than the HCP. The differences were probably due to the different content of hydrophilic compounds in these products, which are capable of binding water [Nyangena et al., 2020].
To estimate the parameters of surface microstructure of the insect powders, the empirically determined isotherms of water sorption were transformed according to the BET model in the aw range of 0.07−0.33. The parameters of the BET model are presented in Table 2. The capacity of the monolayer (vm) is an indicator of the availability of polar sites of the adsorbent for water vapor, regardless of which compound is the source of hydrophilic groups [Ocieczek & Zieba, 2020]. A slightly higher vm value was found for LMP, probably due to its higher protein content. Furthermore, considering the higher position of the LMP isotherm with regard to aw of 0.11−0.33, it is likely that with the increase in water content in the environment, there were microstructural changes in the product, indicating that the shelf-life of the LMP was longer compared to that of the HCP. The development of the surface of the monomolecular layer protects food products due to the absorption of a certain amount of water [Mathlouthi, 2001]. The energy constant (ce) reflects the difference between the enthalpy of monolayer desorption and the enthalpy of liquid adsorbent evaporation. The results obtained for the insect powders (ce ≥ 2) (Table 2) confirmed the sigmoidal shape of the sorption curve. Based on the SKO and RMS values, it was found that the parameters of the BET model described well the sorption process of the insect powders. The RMS error did not exceed 10%, indicating good fit of the model to the sorption data in the water activity range of 0.07−033. The specific sorption area (SSA) is one of the most important parameters characterizing the adsorbents. Among the studied insect powders, LMP had a higher SSA (126.23 m2/g), which was probably due to differences in chemical composition (Table 1) and/or conditions of edible insect processing (especially temperature).
Fat quality of the insect powders
The major fatty acids identified in both LMP and HCP were oleic, linoleic, and palmitic acids (Table 3). Similar fatty acid profiles were obtained by Kowalski et al. [2022a] for both powders and by Roncolini et al. [2020] for LMP. The lipid fraction of LMP exhibited a specific composition, with saturated fatty acids (SFAs), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) at comparable share in the total fatty acids (30.1% 34.5%, and 35.4%, respectively). Consequently, LMP may exhibit lower oxidative stability during storage or baking compared to HCP, which had a higher SFA content (39.8%) and a lower PUFA content (30.9%). Udomsil et al. [2019] reported that fatty acid composition varied in insect species, depending on many factors such as environmental conditions and their diet. Moreover, differences in fatty acid profiles can be attributed to the developmental stage and sex of the insect. For instance, Orkusz [2021] showed that the fat of house cricket larvae contained a higher percentage of unsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs and PUFAs) and lower percentage of SFAs compared to the fat of adult insect. In turn, Kulma et al. [2019] reported that female house crickets had a significantly higher lipid content and slightly higher MUFA levels than males. However, Sushchik et al. [2013] highlighted that the fatty acid profiles of whole bodies or specific tissues change throughout the development from egg to adult, with variations depending on species and diet. Nevertheless, the fat of most edible insects is primarily composed of triacylglycerols, with minor amounts of other lipids such as mono- and diacylglycerols, cholesterol, phytosterols, free fatty acids, and phospholipids [Mlček et al., 2019; Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2014]. Among phytosterols derived from the feed, stigmasterol, β-sitosterol, and campesterol were determined in house cricket fat [Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2021], and stigmasterol and β-sitosterol in fat of mealworm and superworm larvae [Mlček et al., 2019]. Their metabolites including desmosterol, cholesterol, cholestan3-ol, and cholest-7-en-3-ol as well as phospholipids such as phosphatidylcholine (a major phospholipid), phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, sphingomyelin, phosphatidylglycerol, hexosylceramides, and lactosylceramide were also identified in house cricket fat [Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2021]. It is worth noting that phosphatidylcholine is a major component of lecithin, which is used in foods as an antioxidant, taste preservative, and emulsifier.
Table 3
Fatty acid composition and quality parameters of fat extracted from lesser mealworm powder (LMP) and house cricket powder (HCP).
It is proven that edible insects are rich in healthy lipids, including ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids. Notably, the fatty acid composition of edible insects is considered more desirable than that of conventional foods [Udomsil et al., 2019]. The fatty acid composition of house crickets, in particular, is comparable to that of poultry or fish in terms of the content of unsaturated fatty acids [Rumpold & Schlüter, 2013; Tzompa-Sosa et al., 2021]. However, it should be noted that enriching food products with insect-derived ingredients may reduce product stability due to a higher PUFA content. On the other hand, edible insect powders are a source of bioactive compounds with antioxidant activity. Gharibzahedi & Altintas [2023] reported that lesser mealworm larvae oil extracted with n-hexane contained 0.134 mg/g tocopherols (mainly γ-tocopherol), 0.64 mg/g carotenoids, and 3.65 mg/g phenolic compounds.
Fat quality of the insect powders was assessed by determination of the acid value (AV), which measures the free fatty acid content and indicates the degree of fat hydrolysis, and the peroxide value (PV), which measures peroxide content and indicates the degree of fat oxidation (rancidity). For both indices, significant differences (p≤0.05) were found between the powders (Table 3). Fat in HCP was less hydrolyzed, while the fat in LMP was slightly less oxidized. Similar results of PV (0.96−2.21 mEq O2/kg) were noted in house cricket fat extracted by Ugur et al. [2021] and Khatun et al. [2021]. Lower values for both fat quality indices (AV<2.3 mEq O2/kg and PV<0.5 mg/kg) were found for the fat extracted from LMP by Gharibzahedi & Altintas [2023]. However, it was reported that the fat quality changed according to the manufacturing process of edible insect products. For instance, Singh et al. [2020] found that the fat from freezing house crickets at −20°C for 2 h 10 min showed a significantly higher acid value (13.8 mg KOH/100 g product) compared to the fat from house crickets placed in a sterile plastic bag for 3 h 1 min (4.72 mg KOH/100 g product). Also, Hurtado-Ribeira et al. [2023] demonstrated that processing factors, including slaughtering methods (blanching or freezing), drying techniques (oven-drying or freeze-drying), and defatting processes (mechanical pressing or supercritical CO2 extraction), along with their interactions, significantly influenced the oxidation level of the resulting fat and defatted meal from black soldier fly larvae. At present, there are no specific regulations or standards stipulating the quality parameters of fats produced from edible insects. Therefore, the established maximum PV and AV for fish oil (3 mg KOH/g and 10 mEq O2/kg, respectively) and unrefined edible oils (4 mg KOH/g and 10 mEq O2/kg, respectively) are used by researchers as reference points for the quality of edible insect fat [Hurtado-Ribeira et al., 2023; Khatun et al., 2021; Ugur et al., 2021].
Effect of the insect powders on the color of the shortbread cookies
The results of measuring the surface color of the shortbread cookies are shown in Table 4, and the cookies appearance is presented in Figure 2. The incorporation of the insect powders, from both house cricket imago and lesser mealworm larvae to cookie recipes resulted in decreased cookie lightness. The color of the control cookies had the highest L* value (82.93), while the lowest L* value (70.46) was observed for the cookies with 20% HCP. All samples were characterized by negative a* values, indicating the presence of green hues. The lowest value of this parameter (−0.22) was measured for the cookies with the highest HCP percentage in the recipe, showing a shift towards red. The values of the b* parameter were positive, reflecting yellowness in the sample color. The lowest b* value (33.93) was recorded for the control cookies, while the highest b* value (45.08) was measured for the cookies with 20% HCP. The total color differences (ΔE) between the control cookies and the cookies with insect powders ranged from 3.94 to 16.97. The cookies with 10% LMP were the most similar in color to the control cookies, but doubling the amount of this insect powder significantly increased their ΔE. For cookies with HCP, the difference in ΔE depending on the amount of this insect powder in cookie recipe was smaller than for cookies with LMP.
Figure 2
Images of cookies prepared from wheat flour replaced by 10% (A) and 20% (B) of lesser mealworm powder (w/w), and by 10% (C) and 20% (D) of house cricket powder (w/w), as well as control cookies from wheat flour (E).
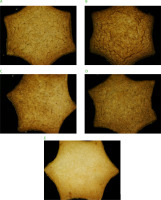
Table 4
Color parameters of cookies prepared from wheat flour (control) and from wheat flour replaced by 10% and 20% (w/w) of lesser mealworm powder (10% LMP and 20% LMP, respectively), and by 10% and 20% (w/w) of house cricket powder (10% HCP and 20% HCP, respectively).
The effect of insect additions on the color of wheat products has been confirmed by other researchers. The study by Zielińska et al. [2021] showed that the incorporation of 2−10% of ground lyophilized insects (mealworm larvae and adult tropical house crickets) into muffins noticeably decreased their b* value, while changes in the a* parameter were insignificant. Pauter et al. [2018] found that increasing the amount of cricket powder (from 5 to 10%) shifted the green/red (a*) and blue/yellow (b*) color balances towards green and blue, respectively. In turn, Sriprablom et al. [2022] noted that higher levels of insect powder substitution (0−30%) significantly increased the redness and yellowness of the cookies. Nevertheless, the cited studies indicated that the lightness decreased with increased insect powder addition. A darker color in wheat products containing insects was also observed by González et al. [2019] (bread), Zielińska & Pankiewicz [2020] (biscuits), Duda et al. [2019] (pasta), and Pauter et al. [2018] (muffins). This decrease can be attributed to the darker color of insect powders compared to wheat flour. Furthermore, samples with a higher amount of protein supplied from the insect powder may have intensified the Maillard reaction occurring at high processing temperatures, resulting in reduced lightness of the baked goods [Sriprablom et al., 2022; Zielińska et al., 2021].
Effect of the insect powders on the fat quality and oxidative stability of the shortbread cookies
Since insect powders are a rich source of fat, it is assumed that their addition alters the fatty acid profile of the final products. Due to the high shares of MUFAs and PUFAs, incorporating both powders increased the contents of oleic, linoleic, and α-linolenic acids in all enriched cookies compared to the control cookies (Table 5). Specifically, there was a 3.3-fold increase in PUFAs in the cookies with 20% LMP. The higher percentages of oleic acid and α-linolenic acid in the LMP than in the HCP (Table 3) resulted in a greater proportion of these acids in the cookies with LMP compared to those with HCP (Table 5). Our results were consistent with those reported by Smarzyński et al. [2021] who observed a slight increase in MUFAs and PUFAs in cookies with 10% HCP. It can be concluded that the use of insect powder significantly enhances the nutritional value of cookies by diversifying the lipid profile and increasing the proportion of PUFAs. On the other hand, it should be noted that a higher proportion of PUFAs can negatively affect the shelf-life of cookies and accelerate oxidation processes. This hypothesis was confirmed by the Rancimat test results (Table 5). The least oxidatively stable were the cookies with 20% LMP. An induction time for these cookies was approximately 1.3 times lower compared to the control cookies (83 h vs. 112 h). Among the cookies with edible insect powders, the longest induction time (102 h) was obtained for those with 10% HCP. Generally, increasing the proportions of oleic and linoleic acids by incorporating edible insect powders correlated with lower oxidative stability of the enriched cookies. Therefore, incorporating natural antioxidant ingredients (e.g., cocoa or spices) or utilizing specialized packaging (e.g., vacuum or inert gas-filled) should be considered during product formulation and shelf-life projection.
Table 5
Fatty acid composition and quality parameters of fat of cookies prepared from wheat flour (control) and from wheat flour replaced by 10% and 20% (w/w) of lesser mealworm powder (10% LMP and 20% LMP, respectively), and by 10% and 20% (w/w) of house cricket powder (10% HCP and 20% HCP).
Effect of the insect powders on the nutritional value of the shortbread cookies
The nutritional value of the control and enriched shortbread cookies is shown in Table 6. The energy values of all types of cookies were similar, in the range of 513–525 kcal/100 g. However, compared to the control cookies, the protein content increased by about 50% in the cookies with 10% LMP and 10% HCP, and by 113% and 100% in those with 20% LMP and 20% HCP, respectively. In another study, a 10% addition of cricket powder increased the protein content in biscuits by 41% [Smarzyński et al., 2021] and by 40.2% in cookies [Bawa et al., 2020]. In addition to increasing the protein content of the product, insect powder also improves the nutritional value of protein due to the full range of essential amino acids it contains [Kowalski et al., 2022a].
Table 6
Nutritional value of cookies prepared from wheat flour (control) and from wheat flour replaced by 10% and 20% (w/w) of lesser mealworm powder (10% LMP and 20% LMP, respectively), and by 10% and 20% (w/w) of house cricket powder (10% HCP and 20% HCP, respectively).
The incorporation of insect powders to the cookies resulted in a significant (p≤0.05) increase in their fat content, with a greater increase noted in the cookies with 20% LMP and 20% HCP, due to the higher fat content of the powders compared to wheat flour (Table 1).
Consumer acceptance of the shortbread cookies with the insect powders
Consumer acceptance is a crucial factor when introducing new products to the food market [Hassoun et al. 2022]. The results of consumer acceptance evaluation of the shortbread cookies with the insect powders are presented in Table 7. This evaluation included the assessment of taste, aroma, surface color brightness and uniformity, consistency, and texture. The shortbread cookies without the insect powder were rated as follows: taste (8.07), aroma (7.54), surface color brightness (9.41), surface color uniformity (8.22), consistency (6.78), and texture (3.80). According to the evaluators, the taste of the control cookies was buttery, characteristic of the raw materials used, and the aroma was sweet and buttery. In addition, the color of the control cookies was the brightest and most uniform. The scores given to the enriched cookies varied and were dependent on both insect type and powder amount added. As the amount of the insect powder in the cookies increased, the scores for taste, aroma, and color decreased; however, the observed differences were not statistically significant (p>0.05). Osimani et al. [2018] and Roncolini et al. [2019] also demonstrated that bread with cricket and mealworm powders had lower consumer acceptance compared to control bread without insect powder incorporation. In a study by Zielińska et al. [2021], lower overall acceptability of muffins with the addition of mealworm larvae and banded cricket powders compared to control muffins was due to lower color, consistency, smell, and taste ratings. González et al. [2019] highlighted that color changes in particular have a significant impact on consumer acceptance of bakery products. Pauter et al. [2018] reported that changes in the color of muffins containing cricket powder were perceived by consumers as unattractive and overly dark. On the other hand, some researchers state that the darker color of bakery and confectionery products is perceived by consumers as typical of health-promoting products, such as those obtained from whole-grain flours [Bawa et al., 2020; González et al., 2019; Pauter et al., 2018]. In the current study, the cookies with LMP received lower scores for surface color compared to cookies with HCP (Table 7). This lower rating could be attributed to the higher content of sugars in LMP, which contributes to Maillard reactions during thermal processing, resulting in a less acceptable color.
Table 7
The consumer acceptability (rating on the linear scale from 1 to 9) of cookies prepared from wheat flour (control) and from wheat flour replaced by 10% and 20% (w/w) of lesser mealworm powder (10% LMP and 20% LMP, respectively) and by 10% and 20% (w/w) of house cricket powder (10% HCP and 20 HCP, respectively).
Edible insects remain a controversial food ingredient, and despite their increasing acceptance, they still have their opponents. It is pointed out that the knowledge of insect content in a food product can lead to lower consumer ratings [Alhujaili et al., 2023]. In addition, insects have a specific taste and aroma, which may not be acceptable to some consumers [Castro & Chambers, 2019]. Therefore, the percentage of insect powder in the final product is crucial. In this study, as the wheat flour replacement by the insect powder increased in the cookie recipes, the sensory evaluation scores decreased. However, these differences were not statistically significant (p>0.05). Kowalski et al. [2022a] showed that only a 30% addition of house cricket powder to bread significantly affected its external appearance, while bread with 10% insect powder achieved full consumer acceptance. The attitude towards edible insects and psychological aspects are also important. In Poland, edible insects are still treated as a new and controversial product. Castro Delgado et al. [2020] conducted sensory studies in Mexico, Spain, and the USA on cookies with 15% and 30% house cricket powder. They reported that Mexican consumers indicated cookies with 30% cricket powder as acceptable as control cookies, which was probably due to greater familiarity and acceptance of edible insects, which ultimately did not affect the psychological perception of taste and aroma by the consumers. Considering the obtained results, further studies may explore the incorporation of aromatic spices or fruits to enhance the sensory properties of the cookies, particularly their taste and aroma.
CONCLUSIONS
The present study discussed the potential application of lesser mealworm and house cricket powders in the production of shortbread cookies. The findings indicated that both insect powders enhanced the nutritional value of the cookies, particularly by increasing protein content and improving the fatty acid profile. The incorporation of lesser mealworm powder enriched the cookies with mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids, notably oleic, linoleic, and α-linolenic acids. The increases in linoleic and α-linolenic acids were more pronounced than those observed with house cricket powder. Neither of the edible insect powders increased fat hydrolysis and oxidation levels in the baked cookies compared to the control products. However, the cookies containing lesser mealworm powder exhibited lower oxidative stability, as indicated by a shorter induction time, compared to those made with house cricket powder, suggesting a potentially shorter shelf-life for this innovative product. Despite this, the sorption properties of both insect powders indicated parameters that could ensure microbiological stability. In turn, consumer acceptance decreased with edible insect powder incorporation in the cookies. Nevertheless, the scores given for individual characteristics generally indicated an acceptable quality for the shortbread cookies produced.

