INTRODUCTION
Increasing global interest in beverages with high functional properties and nutraceutical compounds is gaining momentum [Corbo et al., 2014]. Among these types of beverages, tea and herbal tea are one of the most important in our diets [Liang et al., 2021]. Teas have been found to contain biologically active compounds that can provide health benefits and reduce the risk of chronic diseases [Lorenzo & Munekata, 2016; Sanlier et al., 2018]. Among these phytochemicals, phenolics are natural antioxidants, and their content is significantly correlated with tea antioxidant capacity [Truong & Jeong, 2021]. However, the antioxidant properties of tea are not only related to the presence of phenolic compounds in raw material used for the infusion, but also to the brewing conditions including extraction time and temperature [Sayuti et al., 2021; Xi & Wang, 2013].
Both, the production method and the choice of raw materials significantly influence the antioxidant capacity and phytochemical profile of instant teas [Liu et al., 2021]. Instant teas made from green, black, and dark teas, have been studied by many researchers [Alasalvar et al., 2013; Sinija & Mishra, 2008; Sun et al., 2024]. The criteria for the selection of raw materials for instant tea include availability, processing requirements, and nutritional value. In this context, Rosa canina, also known as rosehip, may have important potential for instant tea production. Rosehip is a perennial plant that belongs to the Rosaceae family. The fruit has a round and long elliptical shape and is generally yellow, red, and orange [Guantario et al., 2024; İpek & Balta, 2020]. About a hundred species of rosehips are found in North America, Asia, and Europe. Meanwhile, 27 varieties of rosehips have been grown in Turkey [Ercişli, 2005]. Recent studies have shown that the vitamin C content of rosehip fruit varies in the range of 100–5,300 mg/100 g, depending on the altitude at which plant is grown, its type and species [İpek & Balta, 2020]. Rosehip fruits are also a rich source of phenolic compounds including phenolic acids, flavonoids and tannins, which determine their antioxidant potential and other bioactivities including antiproliferative, antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects [Mourabit et al., 2023; Nadpal et al., 2016]. The bioactive compounds of these fruits also include carotenoids [Guantario et al., 2024]. Rosehip is widely used in the food industry, medicine, and cosmetics [Negrean et al., 2024].
Drying is another important factor in instant tea production. Phenolic and aroma profiles, and antioxidant capacity are directly affected by the drying process of instant tea [Kraujalytė et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2021]. The commonly employed methods for producing instant tea powder encompass spray-drying, freeze-drying, and vacuum-drying, which are the primary techniques utilized in this process [Someswararao & Srivastav, 2012]. Spray-drying is a well-established and widely used method for converting liquid and semi-liquid food substances into a powder form. This technique has gained considerable attention in the food industry [Anandharamakrishnan, 2013]. Spray-drying is recognized as an effective and unique method for preserving the quality properties of various products, including color, flavor, and nutrients, owing to its short processing time and controlled operational conditions [George et al., 2023]. When producing instant tea powder from tea infusions, the high temperatures involved in spray-drying can alter the content and composition of the aroma compounds through evaporation, oxidation, and thermal degradation [Jin et al., 2023]. This is a major disadvantage of spray-drying. In contrast, the freeze-drying process involves sublimation of ice under vacuum conditions at temperatures below the freezing point of water [Chakraborty et al., 2006]. These low temperatures preserve the aroma of tea by significantly reducing the thermal degradation and evaporation of the compounds responsible for the aroma of tea [Kraujalytė et al., 2016]. In summary, spray-drying is a conventional and cost-effective method for the production of instant tea, while instant tea produced through freeze-drying exhibits a greater abundance of aromatic compounds than that produced by spray-drying.
Based on the information provided, it may be concluded that the application of different drying techniques during instant tea production has an impact on physicochemical quality, phytochemical profile and antioxidant properties of product. To date, most studies on this issue have focused on black, dark, and green instant teas. However, there are very few studies on the instant fruit teas. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine the differences between spray-dried and freeze-dried instant rosehip teas in terms of physicochemical properties, mineral content, phenolic profile and antioxidant capacity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and reagents
Sodium acetate buffer, iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate, 2,4,6-Tris (2-pyridyl)-s-triazine (TPTZ), sodium molybdate, Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). Metaphosphoric acid reagent, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-grade reagents for HPLC analysis and the standard solutions of minerals (Fe, Zn, Cu, Al, Mn, Ca, Mg, Na, and K) used for mineral analysis were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany).
Material
Rosehip fruits from Rosa canina L., which are widely available in various parts of Turkey, were obtained from a local bazaar in Gümüşhane. The fruits were stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until the drying process commenced.
Preparation of instant tea from rosehip fruits
First, the rosehip fruits were dried in an oven (40°C) for 24 h. The dried rosehip fruits with a moisture content of 46.76±1.25 g/100 g (determined by AOAC International method no. 934.06 [AOAC, 2019]) were utilized for extraction under the following conditions: about 4,000 g of the dried fruits were treated with 10 L of boiling distilled water. The mixture was boiled for 10 min and then mixed for approximately 30 min. While still hot, it was filtered through a cheesecloth and placed into 5-L glass jars. The obtained extract was equally divided, with half reserved for freeze-drying and the other half for spray-drying, and then stored in a refrigerator at 4°C until the drying process. The content of total soluble solids of rosehip tea, determined by AOAC International method no 934.06 [AOAC, 2019], was 4.0±0.25°Bx.
Half of rosehip extract volume was added to broad and shallow cups with a capacity of 400 mL, and vacuum was applied under conditions of −65°C and 0.1 mbar in a freeze-dryer (Scientz-12N laboratory lyophilizer, Ningbo Scientz Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China). The product was allowed to dry for 96 h. The weight of the resulting freeze-dried instant rosehip tea was 475.0±11.2 g. Second part of the obtained aqueous extract of rosehip was dried in a lab-type spray-dryer (SD-06 spray, Labplant UK, Hunmanby, England) with a liquid flow velocity of 5 mL/min for 4 h at 200°C, which allowed obtaining 427.0±9.1 g of product. Powders of instant teas were stored until analysis in dark-colored capped bottles at 4°C.
The yield (g/100 g) of the freeze-dried and spray-dried products was calculated according to the formula (1).
where: P is the amount of powder (g) and R is the amount of rosehip (g).Determination of physicochemical properties and mineral profile
For moisture content determination, 5.0 g of rosehip tea powder were taken, weighed in tared aluminum metal cups and pegged at 70°C until constant weight was achieved. The moisture content was provided as g/100 g of instant tea [Nadeem et al., 2011].
A LabSwift-aw water activity meter (Norasina, Lachen, Switzerland) was used to determine water activity (aw) of instant rosehip teas. The samples were then placed in the cup of the device. The aw value was read directly after providing stability to the device.
Color coordinates of instant rosehip teas were determined using a CR-400 Minolta chromameter (Konica Minolta Sensing, Inc. Japan). Approximately 5 g of the instant rosehip sample were placed in the sample container. The values of L* (darkness/whiteness), a* (greenness/redness), and b* (blueness/yellowness) were measured in the CIELab color space. The total color difference (ΔE) between the FD and SD teas was calculated according to the formula (2):
where: ΔL* is the difference between lightness values, Δa* is the difference between greenness/redness values, and Δb* is the difference between blueness/yellowness values of FD and SD teas.For determining water solubility of instant rosehip teas, the powder (1.0 g) was weighed, and 100 mL of deionized water were added at ambient temperature. The mixture was then stirred for 5 min at 600 rpm using a magnetic stirrer. This solution was centrifuged at 3,000×g (NF1200R centrifuge, Nüve Co., Ankara, Turkey). Twenty milliliters of the supernatant were transferred to Petri dishes and left to dry for 24 h at 70°C using an SH-FDO54 oven (Samheung Energy Co., Ltd, Daejeon, South Korea). After drying, the Petri dishes were weighed, and the differences were stated as per 100 g of instant tea [Cam et al., 2020].
A distillation apparatus Vapodest (Gerhardt Vapodest, Gerhardt GmbH & Co. KG, Königswinter, Germany) was used to determine the crude protein content of the instant rosehip teas. Analysis was performed according to the standard Kjeldahl method [AOAC, 2019]. A 6.25 conversion factor was used for protein content calculation. The results were expressed as g/100 g of dry weight (DW) of instant tea.
The ash content was determined using a AOAC International method no. 942.05 [AOAC, 2019]. Instant rosehip powder (2.5 g) was weighed in a porcelain crucible and incinerated at 550oC using a muffle furnace (MF-12, Nuve, Ankara, Turkey). The results were expressed as g/100 g DW of instant tea.
Ash samples obtained during determining the ash content were used for mineral profile analysis. Ashed instant teas were dissolved in 10% nitric acid, and ultrapure water was added until the sample volume reached 50 mL volume [AOAC, 2019]. The microwave plasma-atomic emission spectrometer (MP-AES) (MP-AES system, Agilent Technology, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to determine the metal ions in the solutions. Before measuring, first, a stock solution containing 50 mg/L of the mixed intermediate was prepared by combining separate 1,000 mg/L solutions of Fe, Zn, Cu, Al, Mn, Ca, Mg, Na, and K minerals. Following this, calibration curves with concentrations of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mg/L were prepared using the intermediate stock mixture. The concentrations of minerals in tea solutions measured in mg/L were converted to mg/kg DW of instant tea.
Determination of total phenolic content
For the total phenolic content (TPC) determination, 3.4 mL of deionized water was added to 300 μL of the instant tea solution (200 μg/mL) [Kasangana et al., 2015]. Then, methanol (0.5 mL) and Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (200 μL) were added to the mixture. The mixture was vortexed and incubated for 10 min under ambient temperature, after which 600 μL of a 10% Na2CO3 solution were added. The final mixture was vortexed again and incubated in the dark for 120 min. At the end of the incubation period, the absorbance of the solution was read at 760 nm. The results were presented as mg of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per 100 g DW.
Determination of total flavonoid content
The total flavonoid content (TFC) of rosehip instant tea was quantified in accordance with a method developed by Chang et al. [2002] with slight modifications. A portion of 0.5 mL of an instant tea solution (200 μg/mL) was combined with 0.1 mL of 10% Al(NO3)3 and 0.1 mL and 1 M NH4(CH3COO). The mixture was left to stand at ambient temperature for 40 min. The absorbance was measured against a blank at 415 nm. A series of dilutions of quercetin in methanol was prepared and assayed to prepare a calibration curve. The total flavonoid content in the teas was expressed as mg quercetin equivalent (QE) per 100 g DM.
Determination of ascorbic acid content
The content of ascorbic acid of rosehip instant tea was determined using an HPLC system with a UV detector (Thermo Finnigan, San Jose, CA, USA). Approximately 70 mL of metaphosphoric acid reagent was combined with 10 g of tea powder in a homogenizer. The flask containing the homogeneous mixture was wrapped with aluminum foil to protect against sunlight, and the mixture was then filtered through blue band filter paper [Brubacher et al., 1985]. The filtrate was filtered again with a 0.45-μm syringe filter and transferred to vials for HPLC analysis. The HPLC conditions were as follows: the column was a Supelcosil C18 (5 μm, 250×4.6 mm; Sigma-Aldrich); the mobile phase was methanol – H2O (5:95, v/v) adjusted to pH 3.00 with H3PO4; the column temperature was maintained at 20°C; the injection volume was 20 μL; the detection wavelength was set at 254 nm, covering a range from 210 to 360 nm; and the flow rate was 1.0 mL/min [Ibrahim et al., 2015]. For the calibration curve, standard solutions of L-ascorbic acid were prepared at concentrations of 10, 30, 60, 90, and 120 mg/L. Ascorbic acid content of the sample was calculated in accordance with the linear regression line (y =8467.7x +24.6, R2=0.997) method. The results were expressed in mg/100 g DW.
Determination of antioxidant capacity
Antioxidant capacity of rosehip instant teas was evaluated as total antioxidant capacity (TAC), ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) and as DPPH radical scavenging activity. In all assays, instant teas were dissolved in water at a concentration of 200 μg/mL, and a UV-1800 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) was used to measure absorbance of reaction mixtures.
To determine DPPH radical scavenging activity, 100 μL of a tea solution was combined with 3,000 μL of a 0.1 mM DPPH radical solution. After a 30-min waiting period, the absorbance of the mixture was measured at 517 nm [Brand-Williams et al., 1995]. The results were expressed as mg Trolox equivalent per 100 g DW.
FRAP was determined by Benzie & Strain [1996] method. For the FRAP reagent, a 300 mM sodium acetate buffer solution (pH 3.6), a 20 mM aqueous FeCl3 solution, and a 10 mM aqueous TPTZ solution were mixed at a ratio of 10/1/1 (v/v/v). The FRAP reagent (3 mL), the instant rosehip tea solution (100 μL), and methanol (900 μL) were mixed in a spectrometer cuvette and kept at ambient temperature for 30 min, and absorbance measurements were then conducted at 593 nm. FeSO4 was used to construct a reference curve (62.5–1,000 mg/L), FRAP was expressed as mmol FeSO4 equivalent per 100 g DW.
For the TAC analysis, 2,500 μL of deionized water was added to 500 μL of the sample solution. A molybdate reagent solution (1,000 μL), comprised of 0.6 M sulfuric acid, 28 mM sodium phosphate, and 4 mM ammonium molybdate, was added to the mixture. The mixture was vortexed and incubated in a water bath at 95°C for 90 min. Subsequently, it was kept for 20–30 min until it reached ambient temperature. Purified water was used as a blank sample. The absorbance of the obtained reaction mixture was read at 695 nm [Prieto et al, 1999]. The standard calibration curve was obtained utilizing ascorbic acid (AA). The total antioxidant capacity values were determined in terms of mg of ascorbic acid equivalent (AAE) per 100 g DW.
Phenolic profile analysis
The instant rosehip teas (1.0 g) were dissolved in 25 mL of distilled water. Solutions were filtered using a 0.2 μm microfiber syringe filter and placed in HPLC vials before injection onto the column. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) device (LCMS-8040, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), which was equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source that operated in both negative and positive ionization modes, was used for phenolic compound determination. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a C18 reversed phase column (250×4.6 mm, particle size of 5 μm; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) stabilized at 35°C. The elution gradient consisted of solvents A (5 mM ammonium formate solution in water with 0.1% (v/v) formic acid) and B (5 mM ammonium formate solution in methanol with 0.1% (v/v) formic acid) [Akdeniz et al., 2020]. The following gradient elution profile was used: 20%–100 B (0–25 min), 100% B (25–35 min), and 20% B (35–45 min). The mobile phase flow rate and injection volume were set at 0.5 mL/min and 20 μL, respectively. The operating conditions for the MS were as follows: drying gas (N2) flow, 15 L/min; nebulizing gas (N2) flow, 3 L/min; DL temperature, 250°C; heat block temperature, 400°C; and interface temperature, 350°C. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode was used for the quantification of phytochemicals. Contents of individual compounds in teas were expressed in μg/g DM.
Sensory analysis
A total of twelve panelists (experienced in tea tasting) from the Food Engineering Department of Gümüşhane University (Turkey), six women and six men, examined the instant rosehip teas and evaluated them in terms of flavor, aroma, appearance, color, and overall acceptability, according to previously determined criteria. They evaluated the samples using a nine-point hedonic scale: 1 – dislike extremely, 2 – dislike very much, 3 – dislike moderately, 4 – dislike slightly, 5 – neither like nor dislike, 6 – like slightly, 7 – like moderately, 8 – like very much, and 9 – like extremely. Samples were prepared for sensory analysis based on ISO standards for brewing [ISO8586:2023; ISO 8589:2007; ISO 6658:2017; ISO4120:2021]. Each tea (0.4 g) was taken, 100 mL of boiled water was added, and the samples were placed in porcelain cups. The panelists were given water to rinse their mouths when they passed from one sample to another [Lim et al., 2009]. The findings were calculated as percentages (%). The results of the sensory analysis were presented as a preference map, which was generated using XLSTAT software on the Lumivero platform (Denver, CO, USA). Specifically, the ‘Preference Mapping’ module of the software was employed to visualize the liking levels of each product based on various sensory attributes, highlighting the differences and similarities among the products.
Statistical analysis
All analyses of teas were executed with six repetitions. The results of individual determinations were analyzed using t-test to show significant differences (p<0.05) between FD and SP teas. Moreover, principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to show connections between variables (all determined parameters) and differences among the samples. The XLSTAT software for Excel on the Lumivero platform (Denver, CO, USA) was used for statistical analyses.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Physicochemical properties of the freeze-dried and spray-dried instant rosehip teas
The main physicochemical parameters of instant rosehip tea are shown in Table 1. The instant rosehip teas were obtained by freeze-drying and spray-drying with the yield of 23.75 g/100 g for FD samples and 21.25 g/ 100 g for SD samples. The moisture content and water activity of the FD sample were 9.99 g/100 g and 0.45 g/100 g, respectively. In contrast, the moisture content and water activity of the SD sample were significantly (p<0.05) lower and reached 1.85 g/100 g and 0.26 g/100 g, respectively. According to the literature, the optimal moisture content for instant green tea packaging and storage was reported to be <5 g/100 g [Sinija & Mishra, 2008]. FD tea, in our study, did not meet this requirement. The high moisture content could make it difficult to store.
Table 1
Yield of production and physicochemical parameters of spray-dried (SD) and freeze-dried (FD) instant rosehip teas.
Food processing techniques, such as drying, freezing, curing, and baking, can affect water activity levels. Water activity is a crucial factor in determining the growth of microorganisms and shelf life of food products. Low water activity can result in slow microbiological growth [Tiwari et al., 2014]. The water activity of the instant rosehip teas was relatively low. Comparable values were obtained in a study on green tea extracts; the water activity of microencapsulated green tea extract ranged from 0.36 to 0.28, while the water activity of the free green tea extract was measured at 0.45 [Zokti et al., 2016].
The impact of the drying method on color coordinates of instant rosehip teas was significant (p<0.05). As demonstrated in Table 1, there was a contradiction between the spray-dried and freeze-dried teas with respect to L*, a*, and b* values. These values suggest that the SD sample exhibited a redder and yellower color than that of the FD sample. The lightness of the SD sample was higher than that of the FD sample. The total color difference between the two samples was calculated as 50.74±2.65. the impact of spray-drying and freeze-drying methods was also analyzed in research conducted on carrot waste extract [Seregelj et al., 2021]. The findings indicated that the spray-drying method resulted in lighter-colored products in contrast to the freeze-drying method which resulted in products with darker coloration.
Solubility is a crucial quality parameter for solid food systems because it influences the functional properties of powders. In the present study, the solubility of the FD samples was 87.8 g/100 g, while that of the SD samples was 98.6 g/100 g (Table 1). A statistically significant (p<0.05) difference was observed in the water solubility of both type of teas. Vardanega et al. [2019] investigated powdered tea production from Brazilian ginseng roots using freeze-drying and spray-drying methods. The results showed that the solubility rates were 89% for spray-drying and 90% for freeze-drying. Furthermore, another study compared the effect of different drying methods, including spray-drying and freeze-drying, on the extracts of Thymus serpyllum L. (wild thyme) and found that the powders obtained by spray-drying had higher thermal stability and solubility than those obtained by freeze-drying [Jovanović et al., 2021].
A comparison of the crude protein content of instant rosehip teas obtained using the two different drying methods revealed that the FD product had a crude protein content of 2.22 g/100 g DW, while the SD product had a protein content of 1.86 g/100 g DW (Table 1), with the difference between the products found to be statistically significant (p<0.05). Notably, the protein content of rosehip fruit, as reported in the literature, was 1.60 g/100 g [Fan et al., 2014].
The ash content of the SD sample was found to be 3.87 g/100 g DW, whereas the FD sample had a significantly (p<0.05) higher ash content of 4.12 g/100 g DW. In a study by Özer [2017], ash content for fresh and dried rosehip fruits was reported to be 1.09% for fresh fruit, 2.58% for freeze-dried fruit, and 2.70% for conventionally-dried fruit.
Mineral profile of the freeze-dried and spray-dried instant rosehip teas
In this study, the mineral contents of the instant rosehip teas were determined using an atomic emission technique, and results of analysis are shown in Table 2. As expected, the contents of the macroelements, notably Na, Mg, K, and Ca, were considerably higher than those of the other elements. The Na, Mg, K, and Ca contents of the SD samples were 194; 328; 2,837; and 337 mg/kg DW, respectively. The corresponding values for the FD samples were 261; 339; 3,083; and 340 mg/kg DW, respectively. When the studies in the literature are considered, 11.0 mg/kg for Na, 217.5 mg/kg for Mg, 1,454.5 mg/kg for K, and 844.2 mg/kg for Ca were determined in fresh Rosa canina fruit [Kazaz et al., 2009]. Heavy and/or trace metals such as Cd, Co, Ni, Pb, and Cr were not detected (above the detection limit) in instant rosehip teas in our study. The contents of Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn in the samples were <3.5 mg/kg DW (Table 2). No statistically significant (p≥0.05) differences between the instant tea obtained by spray-drying and freeze-drying were found only for Ca, Mg, and Mn content. Consumers prefer diets rich in specific nutrients that enhance their overall health. The Na, Mg, K, and Ca, which were found in our study in the highest quantities in rosehip instant teas, play important roles in bodily functions. Sodium is essential for maintaining osmotic pressure, extracellular volume, and neuronal excitability, playing a significant role in nerve impulse transmission and muscle function [Bernal et al., 2023]. Magnesium supports over 300 enzymatic reactions, including those involving ATP for energy transfer, and is vital for muscle and nerve function [Fiorentini et al., 2021]. In turn, potassium is critical for maintaining cellular membrane potential and proper nerve function, particularly through the Na+/K+-ATPase enzyme [Abdul Kadir et al., 2018]. Finally, calcium is crucial for bone health, muscle contraction, and nerve transmission, with the majority of the body’s calcium stored in bones [Vaskonen, 2003].
Table 2
Mineral content (mg/kg dry weight) of instant rosehip teas obtained by spray-drying (SD) and freeze-drying (FD).
Total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, ascorbic acid content and antioxidant capacity of the freeze-dried and spray-dried instant rosehip teas
The data on antioxidant capacity, TPC, TFC and ascorbic acid content of instant rosehip teas are presented in Table 3. The TPC of the teas was determined to be 1,495 mg GAE/100 g DW for the FD samples and 1,315 mg GAE/100 g DW for the SD products. The TFC was found to be 146.29 mg QE/100 g DW in the samples obtained through the SD method and significantly (p<0.05) higher (183.67 mg QE/100 g DW) in the samples obtained through the FD method. After reviewing the literature, no studies were found on the TPC and TFC of rosehip-soluble tea. However, according to the literature, the TPC of rosehip fruit powder was 2,482 mg GAE/100 g [Igual et al., 2022]. In turn, TFC of water extracts of fresh and air-dried rosehips was reported to be 1.22 and 1.14 mg QE/g DW, respectively [Nadpal et al., 2016].
Table 3
Total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), ascorbic acid content, and antioxidant capacity measured as total antioxidant capacity (TAC), DPPH radical scavenging activity (DPPH), and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) of freeze-dried (FD) and spray-dried (SD) instant rosehip teas.
Results of ascorbic acid analysis were found as 59.4 mg/100 g DW for the spray-dried tea and as 67.2 mg/100 g DW for the freeze-dried tea, and difference between the samples was statistically significant (p<0.05) (Table 3). In the literature concerning the rosehip fruit, Kazaz et al. [2009] reported the ascorbic acid content at 411.0 mg/100 g for Rosa canina L. and as 332.0 mg/100 g for Rosa damascena Mill. In turn, Fan et al. [2014] performed a study in which they determined the vitamin C content of rosehip fruit to be 426.0 mg/100 g. The same study found that the ascorbic acid content in instant rosehip teas was lower when the powder was dissolved in hot water compared to the rosehip fruit. The researchers explained this by noting that ascorbic acid decomposes in hot water into various compounds such as dehydroascorbic acid and diketogulonic acid. Heat exposure increases the oxidation of ascorbic acid, leading to the formation of these compounds and resulting in the loss of vitamin activity [Pavlovska et al., 2013].
The FRAP of the FD samples was 154.12 mmol FeSO4/100 g DW and that of the SD samples was 133.69 mmol FeSO4/100 g DW (Table 3). DPPH radical scavenging activity of instant rosehip teas was 83.62 mg Trolox/100 g DW in the FD sample and 64.23 mg Trolox/100 g DW in the SD sample. TAC of the samples was determined as 3,804 mg AAE/100 g DW for the freezedried rosehip tea and as 3,338 mg AAE/100 g DW for the spraydried rosehip tea. In a study on the encapsulation of rosehip powder, the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was found to be 1,793 mg TE/100 g [Igual et al., 2022]. In all antioxidant assays, the antioxidant capacity of the FD instant tea was significantly (p<0.05) higher than that of the SP instant tea. This finding is consistent with literature data. A study conducted on papaya puree revealed that samples dried through freeze-drying had a higher content of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity as compared to those dried using spray-drying [Gomes et al., 2018]. The rationale behind this could be that the freeze-drying process operates at low temperatures, thereby minimizing the degradation of sensitive antioxidants and preserving the bioactive components more effectively.
Phenolic profile of the freeze-dried and spray-dried instant rosehip teas
The results of phenolic compounds analyzed by the LC-MS/ MS method in rosehip instant teas dried using freeze-drying and spray-drying methods are given in Table 4. Protocatechuic acid was detected as the main compound for both drying methods (FD: 14.40 μg/g DW, SD: 29.53 μg/g DW). Following this, luteolin 7-glucoside with the content of 6.75 μg/g DW was found in the FD tea, while in the SD sample it was hyperoside with 8.05 μg/g DW. Furthermore, hyperoside (8.05 μg/g DW) and quercitrin (7.14 μg/g DW) were detected only in the samples dried by the SD method. When the literature was examined, it was reported that different quercetin derivatives including rutin, quercetin 3-glucoside, quercetin glucuronide, and quercetin rhamnoside were detected in rosehip fruits [Guantario et al., 2024; Peña et al., 2023]. In another study examining the stability and bioavailability of phenolic compounds of rosehip extracts during in vitro digestion, a total of 34 phenolic compounds were determined using UPLC-MS/MS [Odriozola et al., 2023]. Among these compounds, protocatechuic acid, hyperoside, quercetin, quercitrin, and luteolin 7-O-glucoside were reported at 4.9 μg/g, 73.6 μg/g, 64.6 μg/g, 53.7 μg/g, and 7.8 μg/g, respectively. When comparing these literature data for extracts with those of this study, the results are consistent in terms of the detected compounds, but differ in terms of quantity, which can be explained primarily by the different extraction methods.
Table 4
Retention times (RT), precursor ions and fragment ions of phenolic compounds identified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/ MS) analysis, and their contents in rosehip instant teas obtained by spray-drying (SD) and freeze-drying (FD).
The drying method affected the contents of individual phenolics of instant rosehip teas. The contents of most individual phenolics were significantly (p<0.05) higher in SD tea than in FD tea. The exceptions were chlorogenic acid, luteolin 7-glucoside, luteolin and apigenin, for which higher values were determined in the FD sample. The results of this study are consistent with a study which determined the content of phenolic compounds in papaya pulps dried by FD and SD methods [Gomes et al., 2018]. Oxidative reactions during the drying process affect phenolic losses. While the freeze-drying method can lead to the release of enzymes such as polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase due to low oxygen exposure, the spray-drying method prevents the loss of phenolic compounds by inactivating these enzymes due to high-temperature applications, and more bound phenolic acids are released by the breakdown of cellular components [Gomes et al., 2018]. Therefore, optimizing the drying method and parameters significantly affects product quality in terms of the preservation of bioactive components and antioxidant activity.
Sensory analysis
A food product has to have pleasing appearance, be convenient, and should satisfy consumers’ demands to enter the market and hold on. Sensory analysis can provide information about these subjects. In the total preference mapping scores, the flavor, aroma, and overall acceptability of the FD tea were found to be higher than those of the SD samples. In contrast, the color and appearance of the SD tea were found to be higher (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Preference map for sensory acceptability of instant rosehip teas obtained with spray-drying (SD) and freeze-drying (FD).
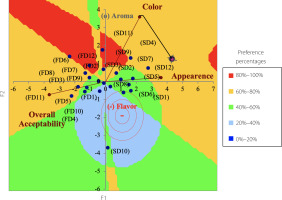
A numerical hedonic scale is useful in evaluation of new products. If a new product reaches a score of 9, 8, or 7, it can be accepted as a suitable product for the market [Pimentel et al., 2016]. In our study, teas obtained with the FD method received 8.67±0.49 points and SD products received 7.00±1.13 points for overall acceptability. Preference map showed distinct differences in the sensory properties of the two instant rosehip tea types produced using different drying methods (Figure 1). The scores were arranged into four areas. The separation between the samples indicated differences in certain investigated sensory parameters. Panelists, in general, preferred the FD tea in terms of aroma and flavor, with a preference rate of 68%, while they preferred the SD tea in terms of appearance and color, with a preference rate of 68% and 64%, respectively.
Multivariate analysis
PCA of the instant tea samples was carried out on the values of 14 quality parameters to identify similarities and differences among them. As shown in Figure 2, the PCA indicated 91.73% of the initial data variability in the total variance.
Figure 2
Plot of principal component analysis (PCA) with distribution of variables including production yield, physicochemical parameters, total mineral content, total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), ascorbic acid content, antioxidant capacity (total antioxidant capacity, TAC; ferric reducing antioxidant power, FRAP; DPPH radical scavenging activity) and color coordinates (L*, a* and b*) of instant rosehip teas obtained by spray-drying (SD) and freeze-drying (FD).
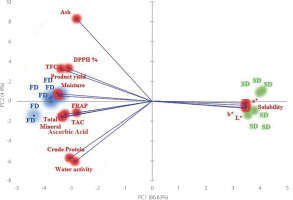
The PCA study revealed that drying methods affected the physicochemical properties, color, and antioxidant capacity of instant rosehip tea. The PCA loading plot also showed that physicochemical, antioxidant, and color properties contributed the most to the scattering patterns of the different drying methods. A clear separation was observed between the spray-dried and freeze-dried teas. Solubility and color coordinates (L*, a*, b*) (maximum in SD tea) contributed the most positively along PC1, whereas ascorbic acid content, FRAP, total mineral, TAC, crude protein content, and water activity (maximum in FD tea) contributed the most negatively along PC1. Product yield, moisture and ash contents, TPC, and DPPH radical scavenging activity (maximum in FD tea) contributed the most negatively along PC2.
CONCLUSIONS
The findings of this study indicate that the method of drying has an impact on the physical and chemical properties, as well as the sensory acceptability, of instant rosehip tea. Both, freeze-drying and spray-drying are effective methods for preserving the bioactive components and physicochemical properties of rosehip instant tea. However, the spray-drying method was found to be less effective in product yield and preserving the ascorbic acid and crude protein contents compared to the freeze-drying method. In addition, the freeze-dried tea showed higher antioxidant capacity. Furthermore, the study found that the negative effect of temperature applied in the spray-drying method on phenolic compounds was limited. The preservation of certain phenolic compounds, such as hyperoside and quercitrin, was aided by spray-drying. The sensory analysis revealed that both freeze-dried and spray-dried instant rosehip teas were well-received, with freeze-dried teas being preferred for their aroma and flavor, while spray-dried teas were preferred for their color and appearance. In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that both freeze-drying and spray-drying are viable options for preserving the main nutrients of rosehip fruit and producing instant rosehip tea for the end consumer.

